Repair and maintenance of vehicles is one of the major business expenses incurred while running an operation. Significant damages are attributed to parking accidents, a common occurrence resulting in costly business repairs.
Even the most experienced drivers are prone to parking accidents which can occur in any type of parking situation, from tight spaces to busy parking lots. It is not just the repair cost that is a concern; a damaged car can result in delays in delivering goods or transporting employees to working stations.
The good news is that parking sensors can help to solve this problem. This article will explain what parking sensors are, as well as highlighting the different types, describing their operation, and listing their benefits.
Table of Contents
What are parking sensors?
Types of parking sensors
How do parking sensors work?
Benefits of parking sensors
Conclusion
What are parking sensors?
Parking sensors are electronic devices that detect the proximity of objects around a vehicle. They warn drivers about obstacles near the vehicles as they park, which helps prevent car damage.
These sensors may be rear parking sensors to help during reversing. However, some drivers may use front parking sensors to make parking much more manageable.
Parking sensors have become more popular owing to the increased vehicle dimensions of newer models and the decreased parking spaces available. Most of them work with rearview cameras to give the driver a visual of the space behind them, displayed on a head unit screen.
Beeping sounds alert the driver when they get close to an object. If the car has a screen, a warning light that turns green to red can warn the driver as they approach an obstacle.
Types of parking sensors
Ultrasonic parking sensors
These parking sensors use high-frequency waves to detect the distance between nearby objects and the vehicle.
Ultrasonic sensors have a diaphragm that vibrates at the frequency of an electric pulse sent by the parking controller. This pulse is activated whenever the driver selects the reverse gear.
Most ultrasonic sensors have an operating range of about three meters. The ultrasonic wave travels over this distance and bounces back to the source once it encounters an obstacle.
The reflected wave then alters the frequency of the diaphragm’s vibration. This new frequency is translated by an algorithm to measure the distance between the car and the object, resulting in beeping sounds or a visual display.
Though ultrasonic sensors are affordable, they have trouble detecting tiny obstacles or materials like plastic.
Electromagnetic parking sensors
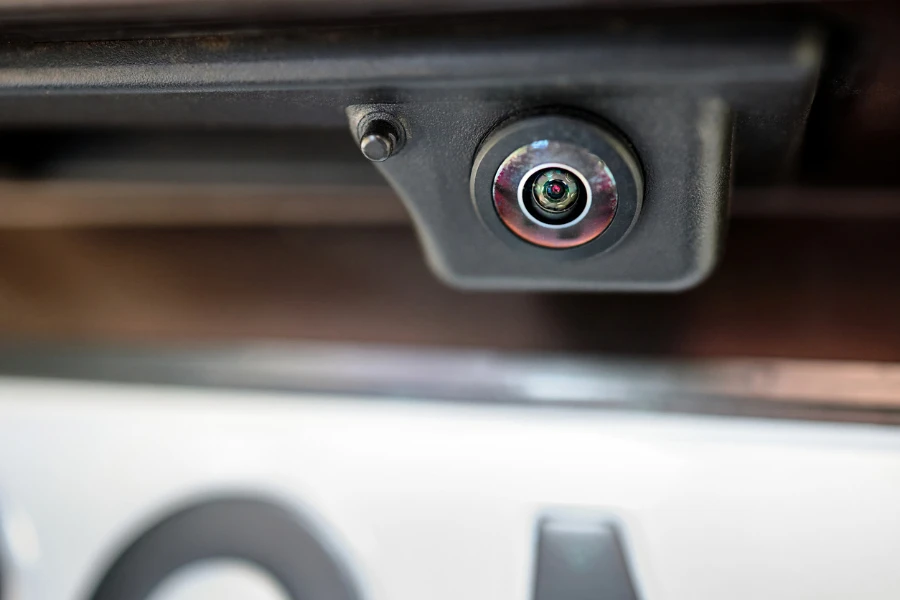

Electromagnetic parking sensors rely on radio waves to detect obstacles. They have a transmitter-receiver unit that produces electromagnetic waves with a characteristic frequency. If they encounter an obstacle, the waves bounce back to the unit at a different frequency.
The receiver then sends this information to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), translating it into distance and speed of approach. This information helps the sensor issue a warning to the driver using either beeping sounds or color changes on display.
Thanks to the broad electromagnetic spectrum, these sensors can detect most materials, making them more reliable than ultrasonic sensors. They can also be hidden, unlike ultrasonic sensors installed externally on different rear bumper parts.
How do parking sensors work?
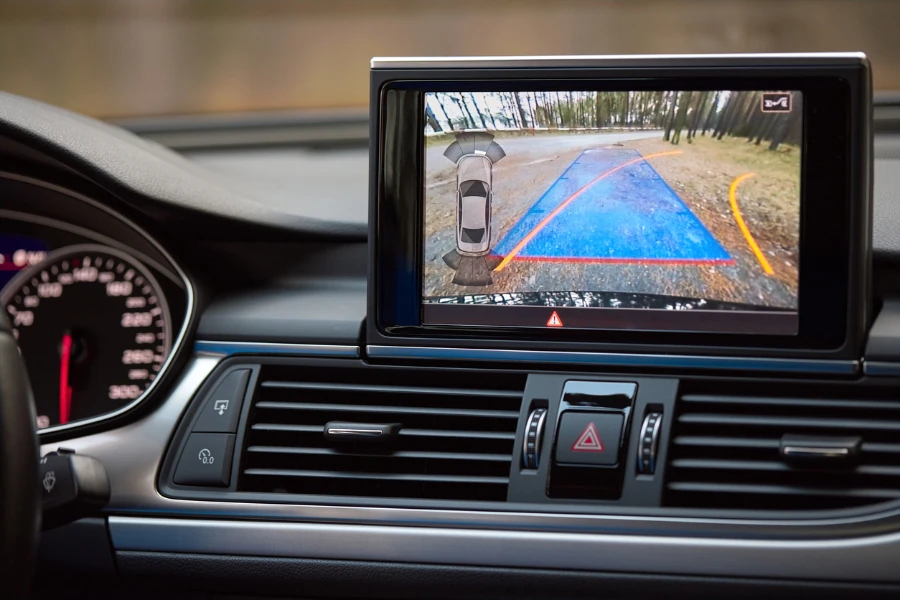

As mentioned above, parking sensors rely on ultrasonic or electromagnetic principles to help them operate.
Ultrasonic sensors are usually triggered by the reverse gear and send ultrasonic signals within a specific operating zone. These signals are reflected in the sensor’s diaphragm, changing its vibrating frequency.
An algorithm in the ECU then translates this information to the distance between the obstacle and the vehicle. Beeping sounds warn the driver of the nearby obstacle, helping them avoid it.
Electromagnetic sensors use the same principles as ultrasonic sensors, but instead of ultrasonic signals, they use electromagnetic waves. Some also incorporate cameras to give drivers an accurate picture of the area around them, improving their parking capabilities.
Benefits of parking sensors
Improved safety
Parking sensors ultimately enhance the safety of drivers and their passengers as they help reduce the likelihood of parking accidents. They alert drivers to obstacles they usually would not have seen, improving parking accuracy.
Parking sensors benefit drivers with babies in their cars because infants are fragile and can be affected even in minor car accidents. This demographic may opt to incorporate parking sensors in their vehicles because of safety assurance.
Reduced damage
Cars with parking sensors are less likely to incur damage from parking accidents because their drivers are warned about nearby obstacles. The beeping sounds from buzzers or color changes on display alert drivers whenever they come close to an object.
Increased resale value
As mentioned before, vehicles with parking sensors are less likely to be involved in parking accidents. As a result, they are more likely to be less damaged and to have their original parts in good working condition, increasing their resale value.
Cost-effectiveness
Investing in parking sensors for vehicles is cost effective for sellers. It is a popular feature that most consumers prefer, making cars that have it sell faster than those that do not. In the long run, it is more profitable than holding on to cars without parking sensors.
Conclusion
Parking sensors have become a popular car feature for consumers. By installing parking sensors for your fleet of vehicles, you reduce the business expense of repair and maintenance, which has ripple effects on running a business operation.
For more details on parking sensor items, visit Chovm.com.





 বাংলা
বাংলা Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Kiswahili
Kiswahili ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt isiXhosa
isiXhosa Zulu
Zulu