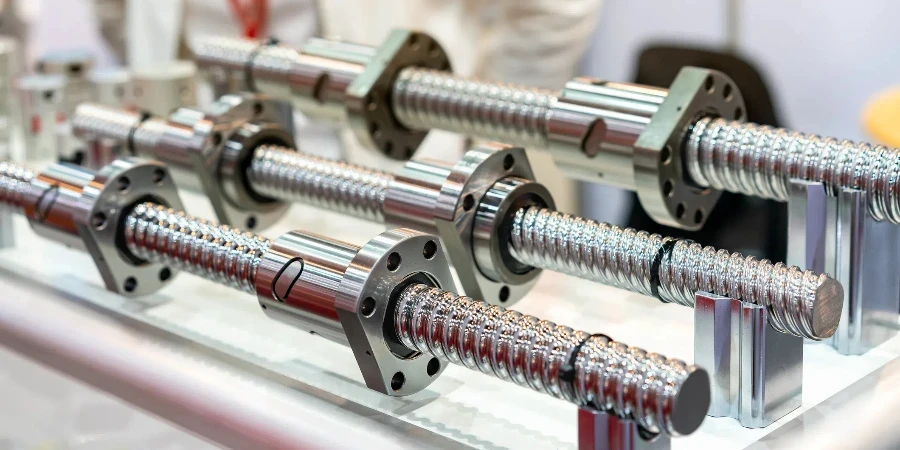
Recent advancements in automation have propelled the Ball Screw market to new heights in 2025. This article delves into the critical aspects of selecting the right ball screw, covering design features, manufacturing processes, and cost considerations. Professional buyers will find valuable insights to make informed decisions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Table of Contents:
-Global Precision Ball Screw Market: An In-Depth Overview
-Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Ball Screw
-Advanced Materials and Technologies in Ball Screws
-Applications of Ball Screws in Modern Machinery
-Maintenance and Longevity of Ball Screws
-Final Thoughts
Global Precision Ball Screw Market: An In-Depth Overview
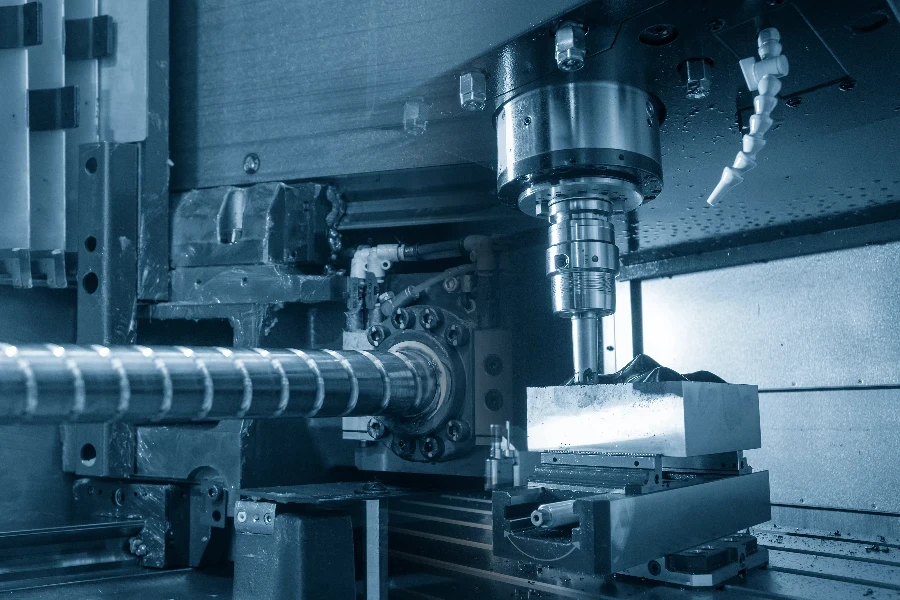
Market Overview
The global precision ball screw market has grown significantly, reaching $1.6 billion in 2023. Projections indicate expansion to $2.3 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.1% from 2023 to 2032. This growth is driven by increasing automation across various industries and the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies. Precision ball screws are critical in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare sectors, valued for their high accuracy and efficiency in converting rotational motion into linear motion.
Asia Pacific holds the largest market share due to rapid industrialization and economic growth in countries like China, Japan, and India. The region’s burgeoning automotive industry and investments in renewable energy and infrastructure projects are also contributing to the heightened demand for precision ball screws.
Detailed Market Analysis
Precision ball screws are essential in applications requiring precise motion control, such as CNC machines, robotics, aerospace, and medical equipment. The market is segmented into ground precision ball screws and rolled precision ball screws. Ground precision ball screws dominate due to their superior accuracy and reliability, crucial for high-precision applications in aerospace, defense, and semiconductor manufacturing. The trend towards miniaturization in medical devices and electronics further fuels the demand for smaller, highly accurate ground precision ball screws.
In terms of application, the semiconductor industry holds the largest market share. The industry’s move towards three-dimensional (3D) integration and advanced packaging technologies necessitates precise alignment and assembly processes, making precision ball screws indispensable. The demand for consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and IoT devices also drives the need for high-precision manufacturing processes that rely on precision ball screws.
Recent innovations include the development of miniature ball screws for smaller devices and the integration of smart features for enhanced performance and reliability. These advancements respond to the industry’s demand for improved productivity, reduced downtime, and superior product quality. As industries continue to prioritize these aspects, the market for precision ball screws is expected to grow considerably.
Key Market Drivers and Trends
- Increasing Automation and Advanced Manufacturing Technologies: Automation is a significant driving force behind the precision ball screw market’s growth. Precision ball screws are extensively used in automated processes, including CNC machines, robotics, and industrial automation systems, where precise positioning and movement control are essential. The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, including additive manufacturing and smart manufacturing, further fuels the demand.
- Focus on Energy Efficiency and Electromechanical Systems: The shift towards energy-efficient solutions is encouraging industries to replace conventional hydraulic and pneumatic systems with electric actuators driven by precision ball screws. These systems offer higher efficiency, reduced energy consumption, quieter operation, and lower maintenance, making them attractive for various applications, particularly in the automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery sectors.
- Rapid Industrialization and Infrastructure Development: Emerging economies are experiencing rapid industrialization and infrastructure development, leading to increased investments in machine tools and industrial machinery. Precision ball screws are crucial in applications such as metal cutting, milling, and assembly processes, driving their demand in regions like Asia Pacific. The growth of industries like electronics, healthcare, and consumer goods in these regions also contributes to market expansion.
As industries continue to explore cutting-edge technologies and demand superior equipment performance, precision ball screws will remain critical in achieving enhanced product quality and operational excellence. The market’s future looks promising, with continuous innovations and a growing focus on energy efficiency and automation.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Ball Screw
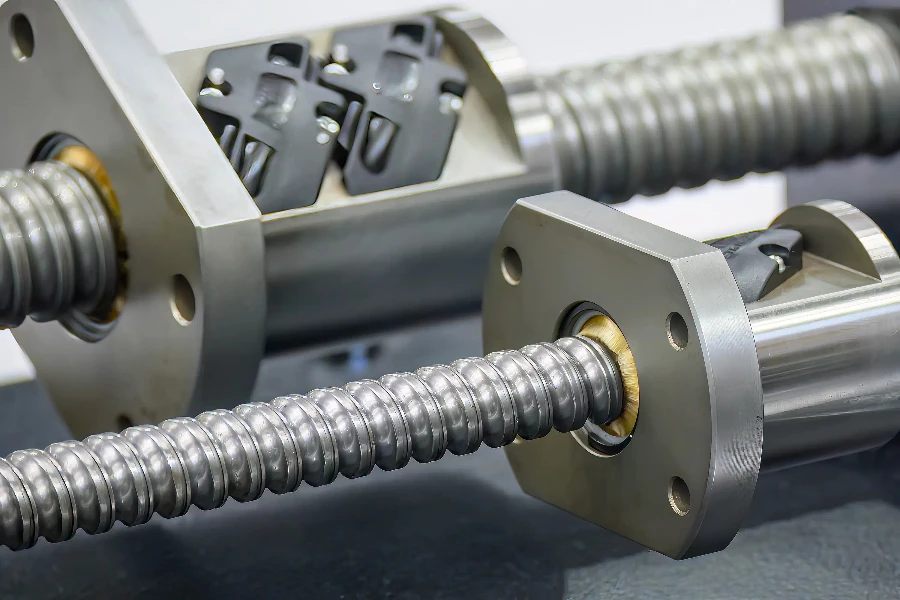
Design Features
When selecting a ball screw, consider various design features that impact performance and suitability. One crucial feature is the zero backlash design, which minimizes axial free motion between the nut and screw, enhancing stiffness and precision. Proper screw lubrication ensures smooth operation and longevity. The choice between right-hand and left-hand threads affects motion direction and system compatibility.
Twin leads are useful in applications requiring opposing dual motion with a single drive system. This design includes both left-hand and right-hand threads, enabling versatile movement. The nut material, typically plastic or bronze, influences wear resistance and performance under different loads. Ensuring these design features align with operational requirements is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of ball screws impacts their accuracy, durability, and cost. There are three primary processes: rolled, milled, and ground. Rolled screws, produced through a cold rolling process, have an accuracy of about 0.004 inches per foot and are cost-effective for general applications. Milled screws, made using a milling machine with an Acme form cutter, achieve higher accuracy of around 0.002 inches per foot, suitable for applications needing moderate precision.
Ground screws, manufactured using a grinding wheel with an Acme form, offer the highest precision with an accuracy of 0.0005 inches per foot, ideal for high-precision applications. Understanding these manufacturing differences helps in selecting a ball screw that meets specific accuracy and performance requirements, balancing cost and functionality effectively.
Physical Specifications
Key physical specifications determine a ball screw’s suitability for an application. The screw length must match the required travel distance. The outer screw diameter affects load-carrying capacity and rigidity. Screw lead, the axial distance a screw travels during one revolution, influences the speed and resolution of linear motion.
The dynamic load rating indicates the load that can be sustained while moving, while the maximum static capacity defines the load supported when stationary. These load ratings ensure the ball screw can handle expected operational loads without compromising performance or safety. Careful consideration of these specifications helps select a ball screw that meets mechanical and operational demands.
Standards and Certifications
Compliance with industry standards and certifications ensures the quality, performance, and safety of ball screws. ISO 3408 establishes the vocabulary and specifications for ball screws, including their designation and nominal diameters. BS 6101-2 applies to recirculating ball screw assemblies made from hardened steel, ensuring durability in demanding applications. Adherence to these standards guarantees that ball screws meet stringent quality criteria for various industrial environments.
Certifications from reputable organizations assure product performance and safety. For instance, ball screws used in aerospace or medical applications may require additional certifications to meet specific regulatory requirements. Ensuring compliance with relevant standards and certifications enhances reliability, facilitates regulatory compliance, and reduces operational failures.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Cost significantly impacts the overall budget of a project. The choice of manufacturing process, material, and design features influences the cost of the ball screw. Rolled screws are cost-effective for moderate accuracy requirements, while ground screws offer higher precision at a premium price. Balancing the need for precision with budget constraints is essential for a cost-effective selection.
Considering the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and potential replacement costs, is crucial. Investing in high-quality ball screws with superior materials and design features may result in lower maintenance costs and longer service life, providing better value for money. Evaluating cost and budget considerations holistically helps select a ball screw that meets performance and financial requirements.
Advanced Materials and Technologies in Ball Screws
Advanced materials and technologies have enhanced the performance and durability of ball screws. One advancement is the use of ceramic hybrid bearings, consisting of steel inner and outer rings with ceramic balls. These bearings offer higher speed and acceleration capability, increased stiffness, and reduced friction and heat generation. Ceramic materials also extend the operating life of ball screws, making them suitable for high-demand applications.
Advanced coating technologies, such as titanium nitride (TiN) and diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings, have improved wear and corrosion resistance. These coatings provide a hard, low-friction surface that extends service life and reduces maintenance requirements. Integrating these advanced materials and technologies ensures reliable performance in harsh environments and demanding applications.
Applications of Ball Screws in Modern Machinery
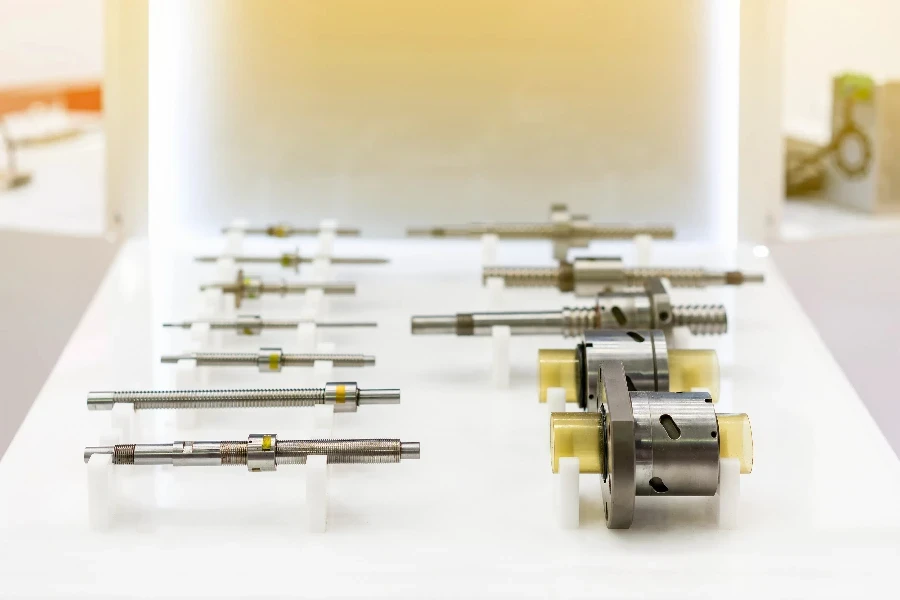

Ball screws play a critical role in various modern machinery applications, providing precise linear motion and high load-carrying capacity. In the aerospace industry, ball screws are used in flight control systems, landing gear actuators, and other critical components requiring high precision and reliability. Their predictable service life and low wear rate make them ideal for safety-critical applications.
In the medical field, ball screws are employed in surgical robots, imaging equipment, and patient handling systems. Their high accuracy and smooth motion enable precise control in medical devices, enhancing the efficacy and safety of medical procedures. Advanced materials ensure ball screws can withstand stringent hygiene and sterilization requirements.
Ball screws are also widely used in industrial automation, including CNC machines, packaging equipment, and assembly lines. Their ability to convert rotary motion to linear motion with high efficiency and precision makes them indispensable in automated systems. Accurate and reliable motion control with ball screws contributes to the productivity and efficiency of modern manufacturing processes.
Maintenance and Longevity of Ball Screws
Proper maintenance is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of ball screws. Regular lubrication reduces friction and wear, preventing premature failure. The choice of lubricant and lubrication intervals should be based on operating conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations. Periodic inspection and cleaning of ball screws help identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
Monitoring backlash and wear is important for maintaining precision and performance. Excessive backlash can indicate wear or damage, necessitating adjustments or component replacement. Implementing a preventive maintenance program that includes regular inspections, lubrication, and adjustments can significantly extend the service life of ball screws, ensuring reliable operation and reducing downtime.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right ball screw involves considering various factors, including design features, manufacturing processes, physical specifications, standards, and cost. Advanced materials and technologies have further enhanced ball screw performance and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of ball screws, contributing to the efficiency and productivity of modern machinery.




