The advent of laser engraving machines has transformed the way we approach material design and customization. From intricate art pieces to industrial-grade parts, the capabilities of these machines are vast and varied. This article aims to explore the five critical aspects of laser engraving machines that users find most valuable. By breaking down complex concepts into understandable insights, we’ll navigate through the technology, applications, material compatibility, maintenance, and cost considerations of these sophisticated devices.
Table of Contents:
– Understanding laser engraving technology
– Applications of laser engraving in various industries
– Material compatibility and limitations
– Maintenance tips for optimal performance
– Cost considerations and value
Understanding laser engraving technology
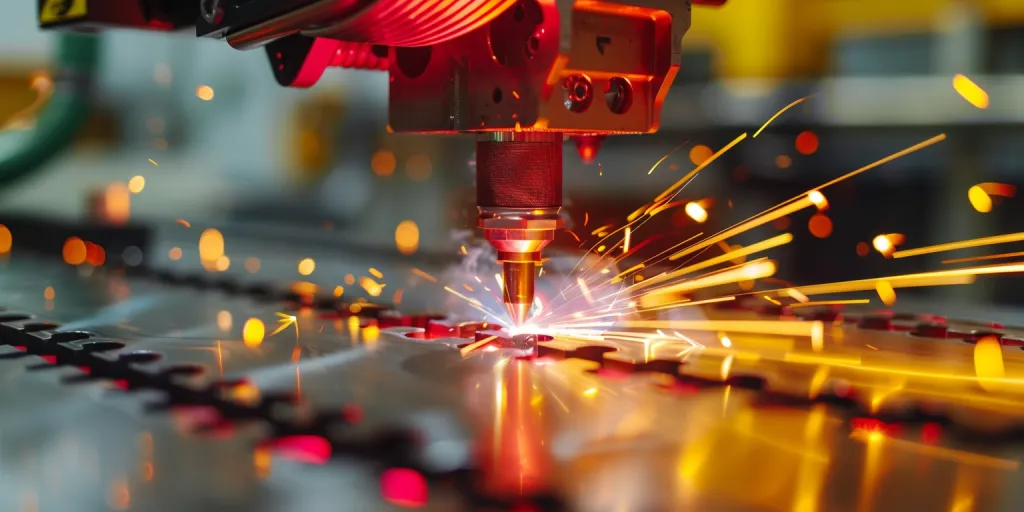
Laser engraving machines operate by using a high-powered laser to etch designs onto various materials. The precision of the laser beam allows for intricate details to be created, which would be impossible with traditional engraving tools. This section delves into the technical details of how these machines work, including the types of lasers used and the importance of software in the engraving process.
The core of laser engraving technology lies in its ability to focus a narrow beam of light with intense energy onto a specific point on the material’s surface. This concentrated energy causes the material to vaporize or burn, leaving behind a permanent mark. The versatility of laser engraving machines is further enhanced by their compatibility with various software programs, enabling users to create or import designs that can be precisely replicated on the chosen material.
Another aspect of laser engraving technology that merits discussion is the difference between engraving, etching, and marking. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to distinct processes that offer different results. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone looking to invest in a laser engraving machine, as it influences the machine’s capabilities and the quality of the final product.
Applications of laser engraving in various industries
Laser engraving machines have found applications in numerous industries, from jewelry design to automotive manufacturing. This versatility is one of their most appealing attributes. This section highlights how different sectors utilize laser engraving for both creative and functional purposes.
In the world of fashion and jewelry, laser engraving allows for the creation of personalized items with intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve by hand. Similarly, in the manufacturing sector, laser engraving is used for part identification, branding, and creating durable markings that withstand harsh conditions.
Moreover, the medical industry benefits from laser engraving’s precision for labeling surgical tools and medical devices, ensuring that vital information remains legible even after repeated sterilization. These examples illustrate the broad range of applications for laser engraving machines, showcasing their adaptability and importance across various fields.
Material compatibility and limitations

One of the most common questions about laser engraving machines concerns the types of materials they can process. This section addresses the compatibility of different materials with laser engraving, including metals, plastics, wood, and glass, and discusses the limitations encountered with certain substances.
Metals, for example, require specific types of lasers, like fiber lasers, for effective engraving. Plastics, on the other hand, vary widely in their reaction to laser engraving, with some producing clean, crisp marks and others melting or distorting. Understanding the interaction between the laser and the material is crucial for achieving the desired outcome and avoiding damage to the machine or the product.
Furthermore, this section explores how advancements in laser technology are expanding the list of compatible materials, offering more creative freedom and application possibilities. However, it also cautions against attempting to engrave materials that are known to release harmful gases or damage the engraving equipment.
Maintenance tips for optimal performance

Maintaining a laser engraving machine is essential for ensuring its longevity and performance. This section provides practical tips on routine maintenance tasks, such as cleaning the lens, checking the alignment of the laser, and ensuring the proper ventilation and exhaust systems are in place.
Regular maintenance not only prevents downtime but also ensures that the quality of the engravings remains high. Neglecting these tasks can lead to costly repairs and subpar results, which is why understanding and implementing a proper maintenance schedule is vital for anyone operating a laser engraving machine.
Additionally, this section highlights the importance of using the correct settings for different materials and projects. Incorrect parameters can not only affect the quality of the engraving but also cause unnecessary wear and tear on the machine.
Cost considerations and value
The final section of this article addresses the cost of laser engraving machines and the factors that influence their price. While the initial investment may be significant, the versatility and efficiency of these machines offer considerable value over time.
This part of the article explores the range of prices for laser engraving machines, from entry-level models suitable for hobbyists to industrial-grade machines designed for continuous, heavy-duty use. It also discusses the potential return on investment, considering the machine’s capabilities to expand business offerings or improve production processes.
Moreover, it provides insights into the cost of consumables and maintenance, which are essential factors to consider when calculating the total cost of ownership. By understanding these financial aspects, users can make informed decisions that align with their needs and budget.
Conclusion:
Laser engraving machines represent a significant advancement in material processing technology, offering precision, versatility, and efficiency. By understanding the technology behind these machines, their applications across various industries, material compatibility, maintenance requirements, and cost considerations, users can harness their full potential. Whether for personal projects or industrial applications, laser engraving machines provide a valuable tool for creativity and innovation.




