L'avènement de l'usinage automatisé avec la technologie de commande numérique (NC) dans les années 1940 et l'automatisation avancée ultérieure permise par les ordinateurs dans les années 1970 ont fait que la fabrication moderne exige une production précise et constante. L'un des outils qui offre systématiquement des résultats et reste très demandé est le tour CNC.
Lisez la suite pour une introduction aux tours CNC, ainsi qu'une description des principaux types de tours sur le marché et de leurs principales applications, afin que vous puissiez être sûr d'offrir à vos acheteurs les meilleures options en 2025.
Table des matières
Qu'est-ce qu'un tour CNC ?
Composants d'un tour CNC
Types de tours CNC
Applications du tour CNC
Avantages de l'utilisation d'un tour CNC
Inconvénients de l'utilisation d'un tour CNC
Tendances futures de la technologie des tours CNC
Conclusion
Qu'est-ce qu'un tour CNC ?
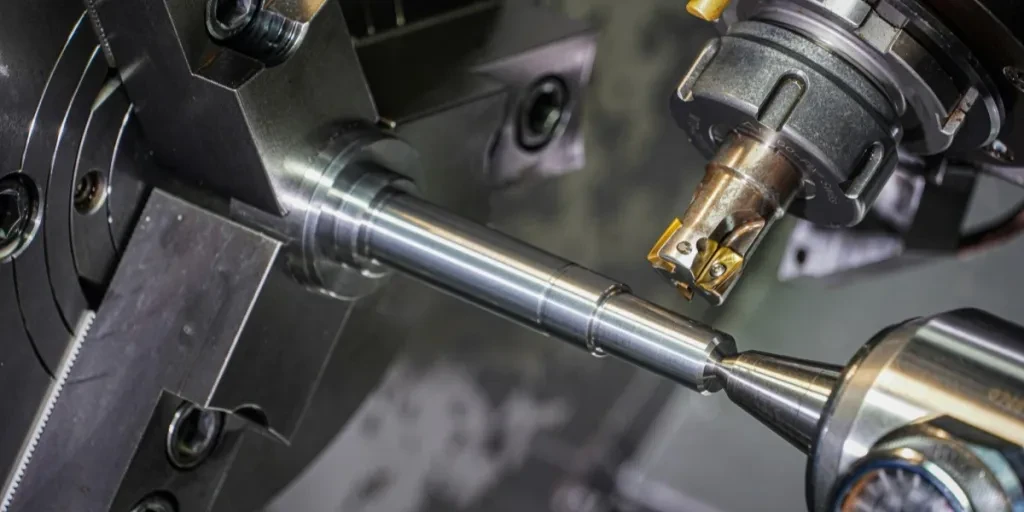
Les tours à commande numérique par ordinateur, ou CNC, sont des machines de précision qui font tourner des matériaux, tels que le plastique, le bois ou le métal, contre un outil de coupe afin de les façonner. tours CNC Les tours CNC se distinguent des tours traditionnels par le fait qu'ils sont contrôlés par des programmes informatiques, ce qui élimine le besoin d'intervention humaine et les éventuelles erreurs humaines. Cette automatisation signifie que le tour CNC est capable de créer des conceptions détaillées, précises et répétables de manière efficace et cohérente.
Composants d'un tour CNC
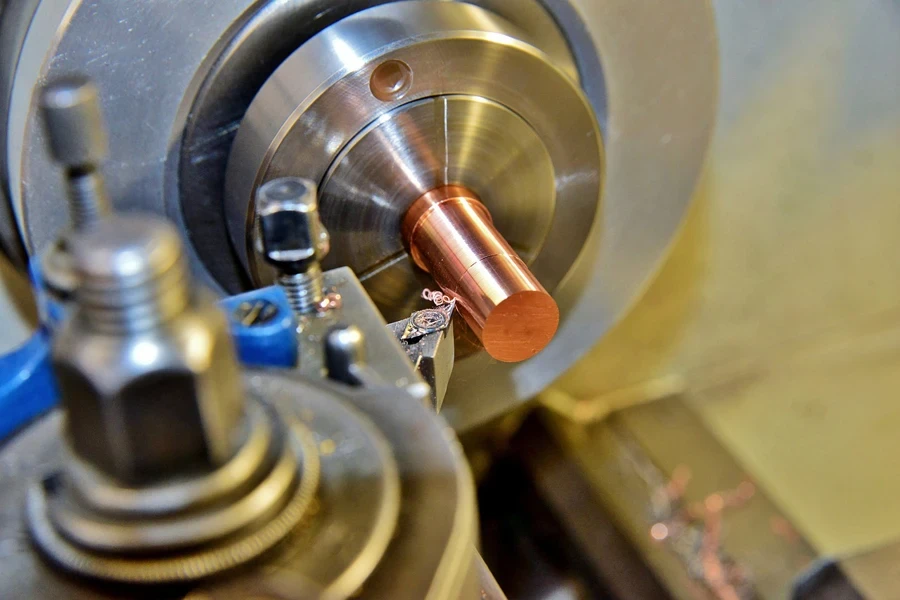
Les tours CNC sont composés de quelques composants clés.
Poupée
La poupée du tour CNC est un élément essentiel pour obtenir une découpe précise de la pièce. Elle contient l'aiguille de la broche principale, qui soutient et fait tourner la pièce, ainsi que le moteur et le mécanisme d'engrenage, qui entraînent la broche et contrôlent la vitesse de la broche, respectivement.
Contre-pointe
Sur le côté opposé à la poupée fixe du tour CNC, la contre-pointe est la pièce qui soutient l'autre extrémité de la pièce à usiner jusqu'à l'aiguille de la broche. Si des travaux d'alésage sont en cours, la contre-pointe est l'endroit où les forets seront situés.
Mandrin
Le mandrin est disponible dans différentes formes et tailles, selon la pièce, et est utilisé pour maintenir cette dernière en place pendant le processus de coupe.
Matelas
Il s'agit de la pièce fondamentale du tour CNC, fonctionnant comme stabilisateur de base pour assurer la coupe douce et précise de la pièce sans interférence des vibrations.
Le chariot
Le chariot est le composant qui abrite l'outil de coupe et le déplace de haut en bas sur la pièce. De plus, le chariot peut parfois contenir d'autres mécanismes qui aident à manipuler l'outil de coupe, notamment le chariot transversal, le tablier et le support d'outil.
Tourelle
La tourelle est un élément rotatif qui agit comme un porte-outil, permettant des changements d'outils rapides avec un temps d'arrêt minimal.
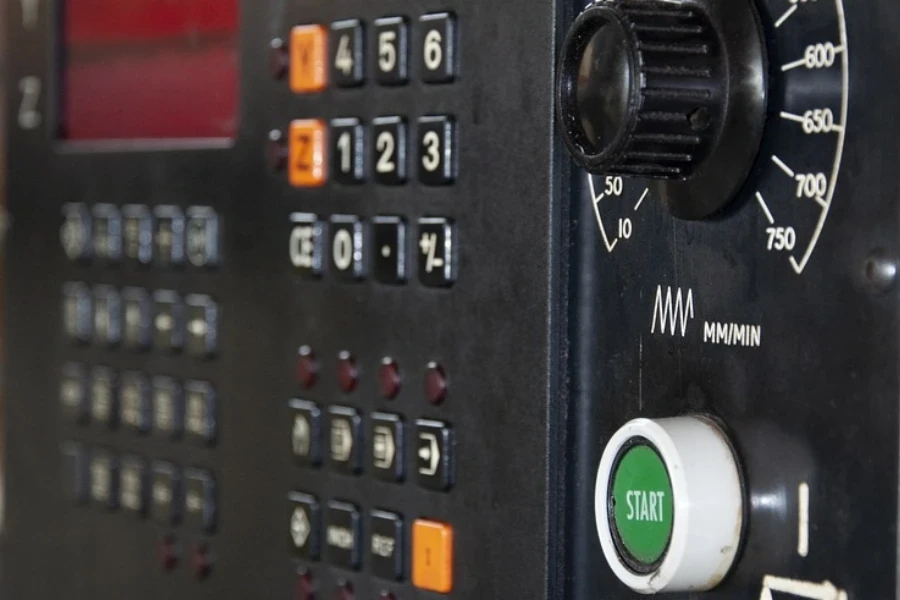
Panneau de contrôle
Comme son nom l'indique, le panneau de commande permet à l'opérateur de saisir toutes les commandes initiales, telles que la vitesse de coupe, la trajectoire de l'outil et le type d'usinage de la pièce. Le panneau de commande est géré à l'aide d'un logiciel tel que G-code ou un logiciel de fabrication assistée par ordinateur (FAO) pour dicter les exigences au tour CNC.
Types de tours CNC
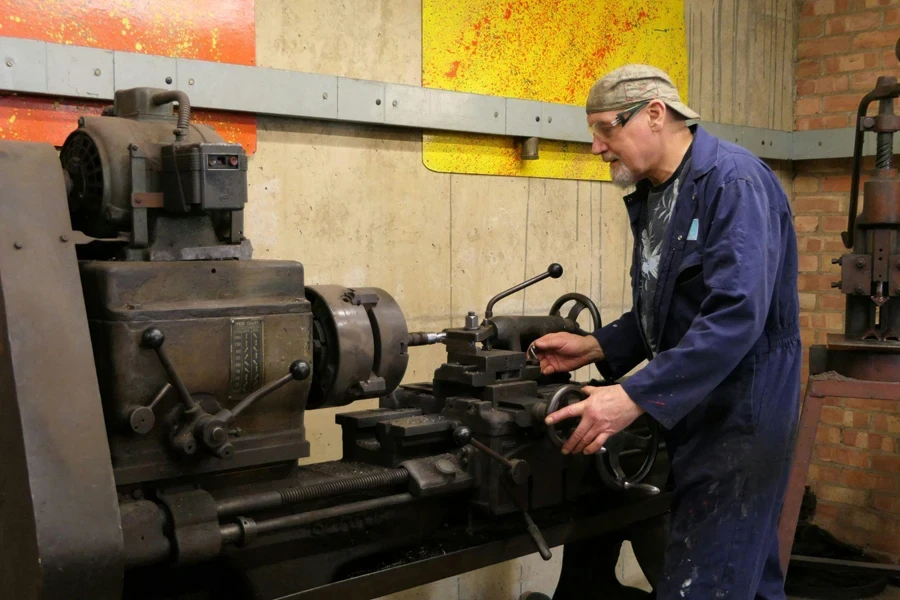

Il existe différents types de tours CNC qui permettent de traiter différentes formes de pièces et différents types de matériaux, différentes exigences de motifs et de coupe et différentes opérations d'usinage. En général, les tours CNC peuvent être divisés en deux catégories :
Tours CNC en fonction du nombre d'axes
Tours CNC à deux axes
Il s'agit des types de tours CNC les plus courants et peuvent être considérés comme la gamme d'entrée de gamme, avec un simple axe X et un axe Z pour contrôler le mouvement de l'outil de coupe. Cette configuration en fait l'un des types de tours CNC les plus abordables et signifie qu'ils sont idéaux pour les tâches simples.
Tours CNC multi-axes
Un type de tour CNC légèrement plus complexe que le tour CNC à deux axes, un tour CNC multi-axes utilise les axes X et Z ainsi que des axes supplémentaires, tels qu'un axe Y ou un axe C. Cela permet des conceptions et des motifs de coupe plus complexes et réduit le temps global si vous entreprenez des tâches plus complexes car cela évite le besoin de plusieurs passes ou configurations.
Tours CNC basés sur l'alignement des pièces
Tours CNC verticaux
Tours CNC verticaux maintiennent la pièce verticalement et, en tant que tels, on les retrouve souvent dans les industries nécessitant la découpe de pièces volumineuses et lourdes, comme dans les industries aérospatiales et énergétiques.
Tours CNC horizontaux
Tours CNC horizontaux Les tours à commande numérique maintiennent la pièce horizontalement et constituent le type de tour CNC le plus courant sur le marché. Ce type de tour CNC est mal adapté aux pièces lourdes ou de grande taille en raison de l'absence de support central et de la possibilité ultérieure de pliage au centre de la pièce.
Applications du tour CNC
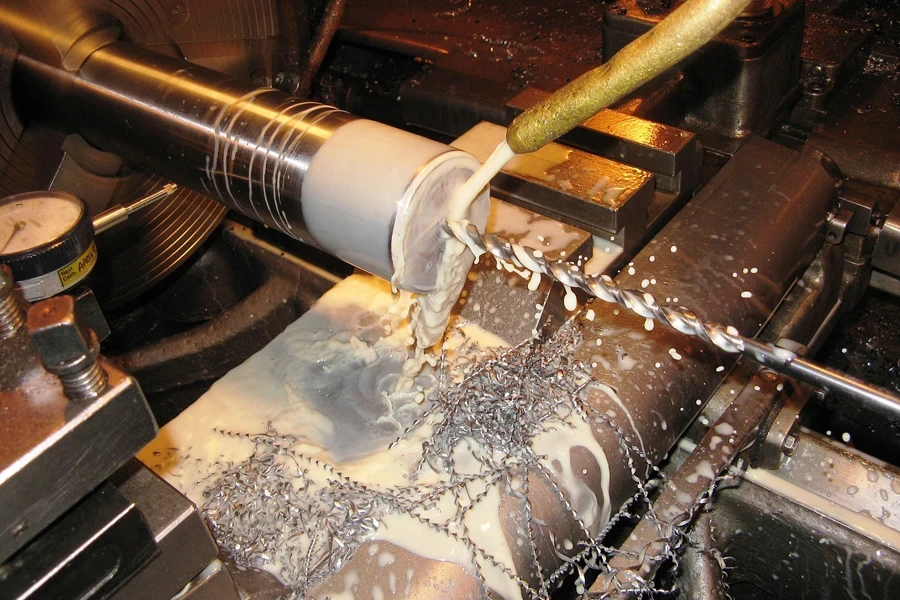

Grâce à l’utilisation de l’automatisation et à leur efficacité, les tours CNC sont utilisés dans de nombreuses industries à haute valeur ajoutée.
Industrie aérospaciale
L'industrie aérospatiale requiert des coupes de haute précision, ce qui fait du tour CNC un outil important pour cette industrie. Ici, les tours CNC sont utilisés pour couper des composants tels que des pales de turbine, des trains d'atterrissage et des pièces de moteur.
Industrie automobile
L'industrie automobile dispose d'une grande variété de machines lourdes qui nécessitent une découpe de haute qualité et précise. De plus, les exigences de production en grande série du secteur impliquent une exigence de rapidité et de régularité, ce qui fait du tour CNC un outil essentiel. Ici, le tour CNC est utilisé pour produire des pièces de moteur, des boîtes de vitesses et des composants de suspension.
la fabrication de dispositifs médicaux
Les dispositifs médicaux doivent être extrêmement précis et, à ce titre, le tour CNC est utilisé dans le processus de fabrication, en se concentrant particulièrement sur les implants, les instruments chirurgicaux et les prothèses.
Fabrication générale
Les tours CNC sont des outils indispensables dans de nombreuses industries manufacturières grâce à leur flexibilité en termes de matériaux et de tailles de pièces à usiner. Parmi les autres secteurs manufacturiers où les tours CNC sont utilisés figurent les biens de consommation et les machines industrielles.
Avantages de l'utilisation d'un tour CNC
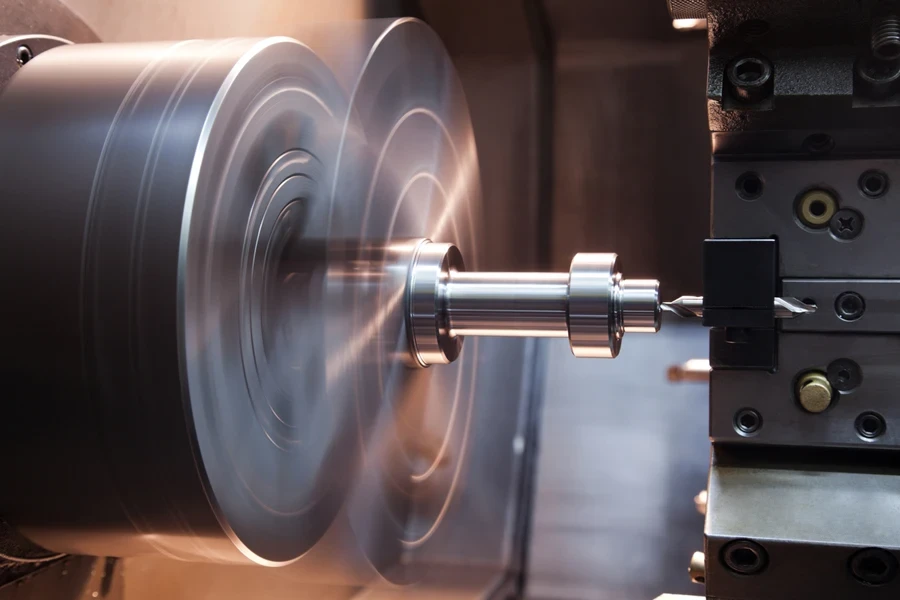
Grâce à leurs multiples avantages par rapport aux outils similaires, les tours CNC sont adaptés à une large gamme d'applications dans diverses industries.
Précision et exactitude
Grâce à leur structure sécurisée, à leur fonction de découpe automatisée et à leurs capacités de déplacement des outils, les tours CNC sont capables de découper des pièces avec une grande précision et de créer systématiquement des pièces de haute qualité. Cela réduit également les risques de défauts et de gaspillage de matériaux, ce qui les rend très efficaces.
Versatilité
Les tours CNC peuvent couper une grande variété de matériaux, notamment des métaux, des composites et des plastiques, selon de nombreux modèles différents. Les outils disponibles sur les tours CNC permettent le centrage, le surfaçage, le tournage, le chanfreinage, le moletage, le filetage, le perçage, l'alésage, l'essorage, le taraudage et le tronçonnage, ainsi que des fonctionnalités supplémentaires.
Vitesse de production
L'automatisation et les options à axes multiples permettent aux tours CNC de fonctionner rapidement et efficacement, sans nécessiter de temps d'arrêt. Cela signifie des temps de production plus rapides.
Coûts de main-d'œuvre réduits
Un autre aspect impacté par l'automatisation est le coût de la main d'œuvre. Comme les tours CNC ne nécessitent une intervention humaine que pour définir les exigences de coupe initiales et les paramètres du tour sur le panneau de commande, le besoin de personnel rémunéré est réduit.
Inconvénients de l'utilisation d'un tour CNC

Malgré les nombreux avantages des tours CNC, il existe également quelques inconvénients. Cependant, ceux-ci peuvent être facilement surmontés.
Investissement initial élevé
Les tours CNC représentent un investissement coûteux et peuvent être difficiles à gérer pour les petites entreprises. Cependant, l'argent économisé sur les coûts de main-d'œuvre et le gaspillage de matériaux grâce à l'utilisation d'un tour CNC compensera l'investissement initial, en particulier lorsqu'il est utilisé dans un environnement de fabrication à volume élevé. Il convient de noter que cet investissement peut ne pas être rentable si les projets requis sont de faible volume ou pour des pièces personnalisées.
Configuration et programmation complexes
Il peut être complexe d'apprendre à configurer et à programmer correctement un tour CNC pour un fonctionnement efficace et précis. Cependant, une fois ces aspects maîtrisés, ces étapes peuvent être réalisées rapidement, ce qui signifie qu'un opérateur peut être utilisé pour plusieurs tours CNC. De plus, les tours CNC peuvent être achetés avec des interfaces simples qui convertissent directement les paramètres accessibles en code G pour la machine.
Maintenance et temps d'arrêt
Bien que l'automatisation des tours CNC permette une production continue avec un temps d'arrêt minimal, cela ne signifie pas qu'il n'y a aucun temps d'arrêt du tout. Il est important d'arrêter la machine à intervalles quotidiens pour effectuer des contrôles généraux et des opérations de maintenance, notamment le nettoyage de la machine, l'inspection du mandrin et de la tourelle porte-outils et la vérification des niveaux de lubrification. De plus, les opérateurs doivent vérifier périodiquement l'alignement de la machine, calibrer les capteurs, inspecter les composants électriques et exécuter des diagnostics de maintenance. Cependant, ces tâches sont courtes et assureront la longévité et le bon fonctionnement de la machine, ce qui permettra par la suite de gagner du temps et de l'argent.
Tendances futures de la technologie des tours CNC
Les tours CNC sont des machines automatisées capables de façonner des pièces rapidement et avec précision grâce à leurs outils et à leurs mouvements faciles. Cependant, à mesure que l'usinage s'intègre de plus en plus à l'IA et à la technologie intelligente, les tours CNC entreront dans la phase de l'industrie 4.0. Cela signifiera moins d'erreurs, des processus d'usinage optimisés, un contrôle qualité amélioré et des capacités de maintenance prédictive, entre autres aspects positifs.
Outre l'intégration de nouvelles technologies, les tours CNC commenceront à fonctionner avec une plus large gamme de matières premières et à résister à des environnements plus extrêmes. Grâce à cela, les tours CNC pourront commencer à être utilisés avec des alliages à haute température, ce qui leur permettra de pénétrer de nouveaux secteurs, par exemple en tant que fabricant de machines-outils dans des secteurs aux conditions extrêmes ou volatiles.
Conclusion
Les tours CNC sont des machines largement utilisées qui offrent précision, rapidité et polyvalence dans de nombreux secteurs industriels. Leur haut niveau d'automatisation permet de réduire les coûts de main-d'œuvre et le gaspillage de matériaux, ce qui en fait un choix idéal pour les entreprises qui exploitent des lignes de production à haut rendement qui exigent qualité et cohérence.
À l’avenir, à mesure que les tours CNC seront intégrés aux technologies d’IA, ces machines seront mieux à même de prédire les problèmes et de les résoudre, ainsi que de produire des conceptions de meilleure qualité et plus complexes. Les tours CNC sont aujourd’hui une machine de fabrication essentielle et ne feront que gagner en importance avec l’essor de la fabrication moderne, ce qui en fait un choix d’investissement judicieux.





 বাংলা
বাংলা Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Kiswahili
Kiswahili ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt isiXhosa
isiXhosa Zulu
Zulu