Different types of thread rolling machines are available in the market. These machines have different capabilities and prices. Demand for thread rolling machines has been increasing over the years, which is why many manufacturers are striving to meet the demand. The availability of many brands of thread rolling machines makes it hard to find the perfect thread rolling machines.
This article will discuss the different types of thread rolling machines available and how to select a suitable machine. Additionally, it will talk about the market share of the thread rolling machines market and the machines’ process.
Table of Contents
Overview of thread rolling machines market
Thread rolling process
Types of thread rolling machines
Guide to selecting suitable thread rolling machines
Summary
Overview of thread rolling machines market
The global thread rolling equipment market is segmented based on the type of machines, by industry of application, and by region. Over the next five years, the market is expected to rise considerably due to the increased inclusion of technological innovations on the machines by key players in the market. Some of these manufacturers are Tsugami China, Nakamura Jico Co. Ltd., and Tobest.
Based on an OEC report in 2020, the global thread rolling machines market was valued at USD 93.4 million. This represented a 21.6% drop from the USD 119 million value in 2019. This drop in market value was due to the reduced adoption of thread rolling machines across the globe. However, the demand for these machines is expected to grow as a result of a variety of applications like automotive, electronics, and medical.
In 2020, the top exporters of thread rolling machines were Italy at USD 18.1 million, Taiwan at USD 17.4 million, Japan at USD 16.4 million, China at USD 11.8 million, and Germany at USD 9.86 million. The top importers were China with a value of USD 14.4 million, the U.S. at USD 10.8 million, India at USD 6.01 million, Thailand at USD 5.91 million, and South Korea at USD 3.52 million.
Thread rolling process
Generally, thread rolling is a metal forging process where a machined blank is pressed between rotating dies. The blank’s thread profile is ground into the dies. As the blank is penetrated by the dies, the metal flows into the die cavities. This results in a thread profile into the workpiece. A cut thread interrupts the part’s grain structure while cold working a rolled part strengthens it. To obtain an appropriate outer diameter (0.375 inches), blanks should be machined or ground into a specific pitch diameter in advance of thread rolling.
The common thread processes include:
– Thru-feed: thread rolling of parts with long thread lengths that exceed the dies’ width.
– Infeed: parts thread rolling where the thread length is shorter than the dies’ width.
– Infeed/thru-feed: a two-step thread rolling for long thread lengths in which partially or incompletely formed threads are reduced.
Types of thread rolling machines
1. Flat die thread rolling machine
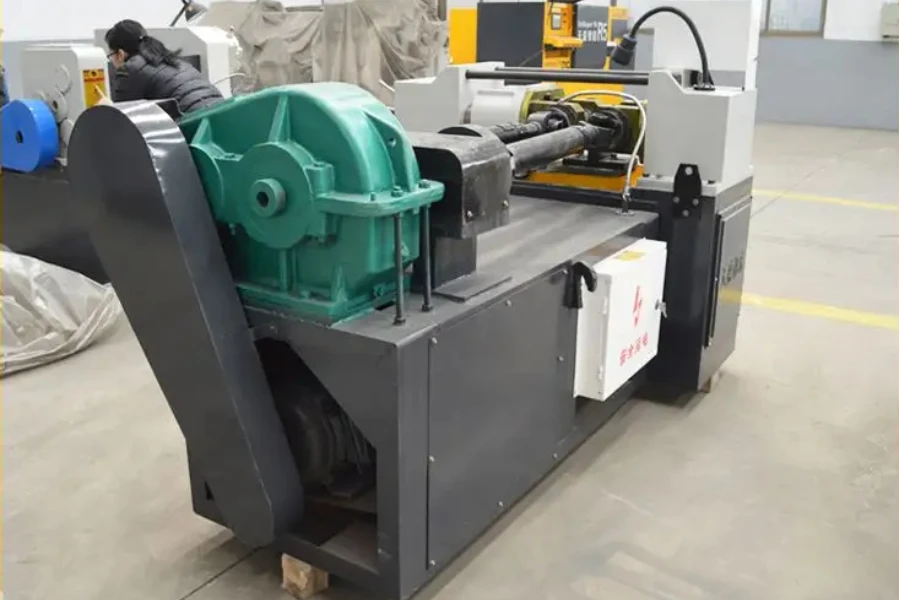

A flat die thread rolling machine has four main parts which include a conductor bar, pusher arm, and two flat dies where one is fixed and the other is moved backward and forward by a crank-type mechanism. The flat dies come with a thread profile machined into them and another thread profile inclined by the pitch of the thread they can create.
The blanks to be threaded are held by the conductor bar, which ensures they are kept in the right orientation. Also, the conductor bar is inclined in a position that when it engages with the blanks, gravity pulls them down towards the pusher arm. The pusher arm forces the blanks into a void between the moving and stationary flat dies. A thread is created when the moving die moves forward and the blanks roll due to the frictional forces of the process.
2. 2-die cylindrical thread rolling machine
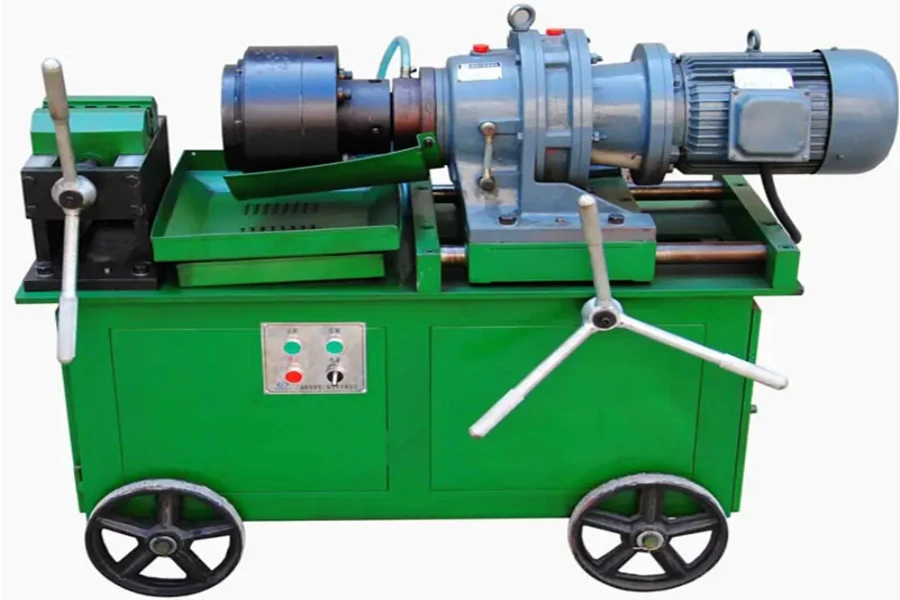

A 2-die cylindrical thread rolling machine has three variations which include infeed, thru-feed, and a combination of infeed & thru-feed. Infeed machines have two parallel dies that rotate in the same direction and at the same speed. One die is fixed while the other has lateral movements. The rolling process depends on friction to rotate the blank. In this case, the lateral movement is adjusted to set the thread pitch and diameter.
Long threaded sections like lead screws and studding are created by the thru-feed process. Notably, large threads require more than one pass to produce complete threads. There are combination machines that can allow for both infeed and thru-feed thread rolling processes.
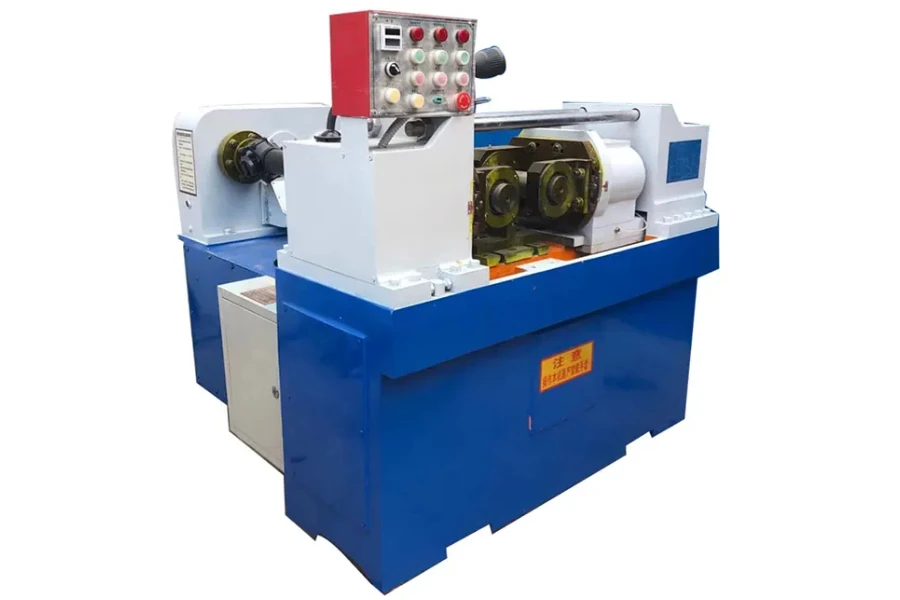
3. 3-die cylindrical thread rolling machine
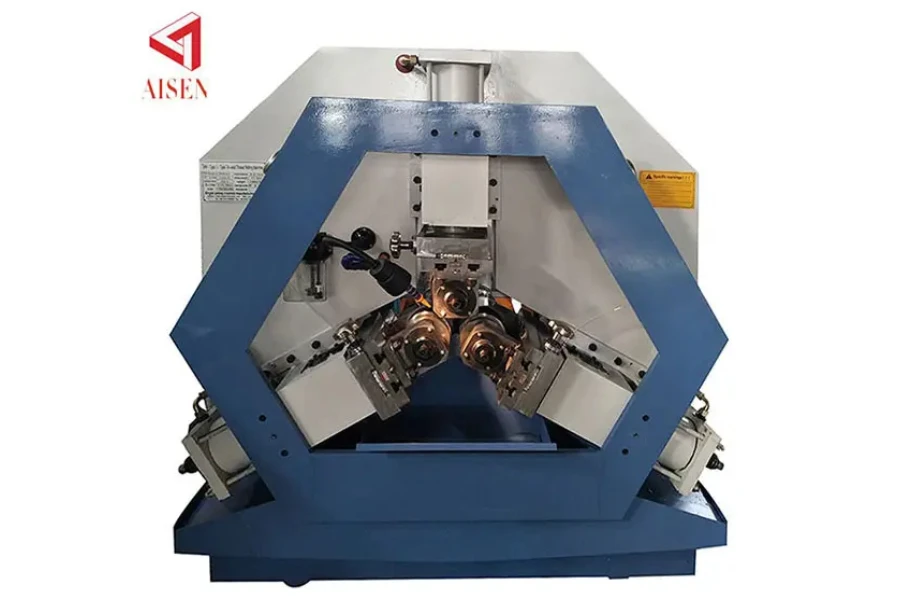
A 3-die cylindrical thread rolling machine comes in three variations. Two of the three dies are fixed while the third moves vertically or laterally based on the layout of the machine. The 3-die cylindrical thread rolling machine is selectively suited for long threaded items like lead screws.
4. Planetary thread rolling machine

A planetary thread rolling machine has the blanks fed into the dies like in a flat die thread rolling machine. The machine has two dies where the circular die rotates and the curved die is fixed. Some planetary thread rolling machines contain multiple curved segment dies mounted around the circular die. This feature ensures high production rates.
Guide to selecting suitable thread rolling machines
1. Cost
Cost includes the initial purchasing price, the cost of accessories, and the equipment maintenance costs. On average, thread rolling machines are available at prices of about USD 5,000. The material being threaded and the demand of the production line determines the kind of thread rolling machine to be purchased. Buyers should consider their budget when investing in efficient thread rolling equipment. Furthermore, they should generally ensure a no scrap, lower tool cost, and lower labor formula to significantly reduce the costs.
2. Precision
The final quality of the rolled thread is dependent on the precision of the thread rolling machine. Apart from material choice, accuracy is determined by the preparation process of the blanks to be threaded. Conventionally, thread rolling displaces material, thus the diameter of the blank is generally smaller than that of the finished rolled thread’s diameter. In this case, the average precision can be achieved if the blanks are machined at tight tolerances of about 0.0005 inches. There is a further recommendation to include a 37-degree chamfer threaded at the end of each section to reduce the risk of chipping and an approximately 45-degree final chamfer.
3. Strength
The inclusion of cold working in thread rolling increases tensile strength by at least 30% more than cut threads. Rolled threads have an improved fatigue strength ranging from 50% to 75%. In this case, threads exhibit no loss of fatigue strength even if they are heated up to 500 degrees Fahrenheit. Some machines produce stronger threads that do not require expensive outside heat treatment. Generally, rolled threads are smoother and are damage-resistant when being handled.
4. Speed
The speed of thread rolling can go up to 200 feet per minute when working on materials like high-carbon steel and brass. However, buyers can obtain better results by employing slower speed. Thread rollers can achieve significant speed when the roller held in a holder is attached to the cross-slide while being presented radially or tangentially. The speed is slower if the roller is held on a swing stool. This is because of a lack of rigidity of the holder on the swing type.
5. Applicable material
It is vital to select a suitable material to enhance the accuracy and quality of the threads produced. Generally, if the material is hard, it becomes equally hard to be rolled, which might affect the service life of the dies. Also, as buyers purchase thread rolling machines, they should note that hollow profiles result in blank ovals due to the forces involved. On average, a suitable material should have a minimum elongation of 12%, a maximum hardness of about 40 HRC, and a maximum tensile strength of 1079 MPa. Furthermore, to improve the dies’ durability, some have coatings like CVD and PVD.
Summary
Thread rolling machines are generally cost-effective due to the prolonged service life of dies. With a minimal requirement for maintenance, the machines have relatively high rates of production. In addition to the factors mentioned in the above guide, buyers should consider the universal standards set for pitches and thread sizes. To acquire quality thread rolling machines, visit Chovm.com.





 Afrikaans
Afrikaans አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Kiswahili
Kiswahili ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt isiXhosa
isiXhosa Zulu
Zulu