In 2025, the demand for energy-efficient solutions has surged, with heat pump water heaters (HPWH) at the forefront. This article delves into crucial aspects such as performance, capacity, and technological advancements, providing professional buyers with valuable insights to make informed decisions. Discover how to optimize your inventory with the best HPWH options available.
Table of Contents:
– Market Overview of Heat Pump Water Heaters
– Detailed Analysis of Heat Pump Water Heater Market
– Key Factors When Selecting a Heat Pump Water Heater
– Assessing Long-Term Costs and Savings
– Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
– Compatibility with Existing Systems and Future Upgrades
– Final Thoughts on Heat Pump Water Heaters
Market Overview of Heat Pump Water Heaters
The global heat pump market has shown significant growth, rising from USD 436.99 million in 2023 to USD 473.61 million in 2024. This market is expected to continue growing, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.83%, reaching USD 790.65 million by 2030. Heat pump water heaters (HPWH) are gaining traction due to increasing energy efficiency requirements, government incentives for renewable energy, and growing awareness of carbon footprint reduction. Technological advancements have also improved the performance and affordability of heat pumps, further driving market growth.
The Americas hold a significant market share, driven by strict regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and substantial government incentives. The U.S. market, in particular, favors air-source heat pumps, especially in residential applications. The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market, fueled by rising energy demands, urbanization, and a focus on sustainability. Europe leads in adoption, with high installation rates of both ground-source and air-source heat pumps in new residential constructions. The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets with growing potential due to increasing urbanization and the need for sustainable heating solutions.
Detailed Analysis of Heat Pump Water Heater Market

Key Performance Benchmarks
Heat pump water heaters are vital in residential, commercial, and industrial applications due to their energy efficiency and environmental benefits. The efficiency of HPWHs is measured by their Coefficient of Performance (COP), typically ranging from 3 to 4. This means they can produce three to four times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume, significantly surpassing traditional water heaters, which usually have a COP of less than 1.
Market Share Dynamics
The market features a diverse range of players, including established brands like Daikin Industries, Mitsubishi Electric, and Carrier Corporation. These companies continue to innovate, focusing on enhancing the COP of their products and integrating smart technologies for better energy management. The residential sector dominates the market, accounting for approximately 60% of the total market share, driven by increasing consumer awareness and government incentives. The commercial sector, including hotels and educational institutions, also represents a significant share due to the need for efficient and reliable water heating solutions.
Economic Influences and Consumer Behavior Shifts
The rising cost of traditional energy sources such as oil and gas is a key driver for HPWH adoption. Consumers are increasingly opting for energy-efficient and eco-friendly solutions to reduce their utility bills and carbon footprint. Government initiatives and incentives play a crucial role in this shift, with policies promoting renewable energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. For example, in the U.S., federal tax credits and state rebates have made HPWHs more accessible and attractive to consumers.
Distribution Channel Preferences
The distribution channels for HPWHs include direct sales, distributors, and online platforms. Direct sales and distributors dominate, accounting for over 70% of the market share. However, the rise of e-commerce platforms is gradually changing the landscape, offering consumers a convenient way to compare products and prices. Online sales are expected to grow significantly, driven by increasing digitalization and consumer preference for online shopping.
Recent Innovations
Recent innovations in HPWH technology include the development of hybrid heat pumps, which combine air-source and ground-source technologies to improve efficiency and performance in varying climatic conditions. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled heat pumps, allows for remote monitoring and control, enhancing user convenience and energy management. Companies like Daikin and Mitsubishi Electric have introduced models with advanced features, such as variable speed compressors and improved heat exchangers, to further boost efficiency and performance.
Customer Pain Points and Brand Positioning Strategies
Despite the advantages, the high upfront cost of HPWHs remains a significant barrier to adoption. The initial investment, including installation and retrofitting costs, can be substantial, deterring some consumers. Additionally, dependency on climatic conditions for optimal performance can be a concern in regions with extreme temperatures. To address these pain points, companies are offering financing options, extended warranties, and comprehensive after-sales services. Brand positioning strategies emphasize long-term cost savings, environmental benefits, and technological advancements to attract and retain customers.
Niche Markets and Differentiation Strategies
Niche markets for HPWHs include off-grid installations, rural areas, and regions with high electricity costs. Companies are developing specialized products for these markets, such as solar-assisted heat pumps and compact models for smaller homes. Differentiation strategies focus on innovation, energy efficiency, and smart technology integration. Brands like Carrier and Viessmann are investing in R&D to introduce cutting-edge products that stand out in terms of performance, reliability, and user experience.
Key Factors When Selecting a Heat Pump Water Heater

Choosing the right heat pump water heater requires understanding several factors that influence performance, efficiency, and overall value. This section explores the critical aspects to consider when selecting a heat pump water heater.
Performance and Efficiency
Performance and efficiency are crucial when evaluating heat pump water heaters. The efficiency of these systems is often measured by their Coefficient of Performance (COP), which indicates the ratio of heat output to energy input. A higher COP signifies better efficiency. Modern heat pump water heaters typically have COPs between 2.5 and 3.5, meaning they generate 2.5 to 3.5 units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed.
Additionally, the Energy Factor (EF) reflects the overall energy efficiency of the water heater. Contemporary models achieve EF ratings of 3.0 or higher, significantly outperforming traditional electric water heaters. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is also useful for assessing performance in varying climate conditions. Systems with higher SEER ratings adapt better to seasonal temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent efficiency throughout the year.
Capacity and Size
The capacity of a heat pump water heater is crucial for meeting household or commercial hot water demands. Residential models typically range from 50 to 80 gallons, while commercial units can exceed 100 gallons. It’s essential to match the capacity to the specific needs of the application to avoid underperformance and unnecessary energy consumption.
Size also matters in terms of physical dimensions, as heat pump water heaters require sufficient space for installation and airflow. They typically need more room than conventional water heaters due to their compressor and evaporator components. Installation guidelines often recommend a minimum of 1,000 cubic feet of space to ensure optimal operation and prevent overheating.
Technological Features
Advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the functionality and user experience of heat pump water heaters. Features like Wi-Fi connectivity and smart home integration allow users to monitor and control their water heater remotely. This capability can lead to energy savings and greater convenience, as users can adjust settings based on real-time usage patterns.
Modern heat pump water heaters often include advanced diagnostics and self-cleaning functions, which help maintain efficiency and prolong the unit’s lifespan. Some models also feature variable speed compressors and fans, which adjust operational intensity to match demand, optimizing energy usage.
Build Quality and Materials
The construction and materials used in heat pump water heaters are critical for durability and longevity. High-quality models typically feature stainless steel or corrosion-resistant tanks, which can withstand harsh water conditions and reduce the risk of leaks.
The insulation type and thickness also play a role in maintaining heat retention and overall efficiency. Polyurethane foam insulation is commonly used for its superior thermal properties, helping to minimize standby heat loss. Robust outer casings and protective coatings enhance the unit’s resistance to physical damage and environmental factors.
Initial Setup and Installation Complexity
The complexity of installing a heat pump water heater can vary significantly based on the model and site conditions. While some units are designed for straightforward installation, others may require professional setup, including modifications to existing plumbing and electrical systems.
Proper installation is crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Factors like adequate ventilation, correct placement, and precise electrical connections must be considered. In some cases, additional components such as condensate pumps or desuperheaters may be needed to manage condensate and improve system integration.
Assessing Long-Term Costs and Savings
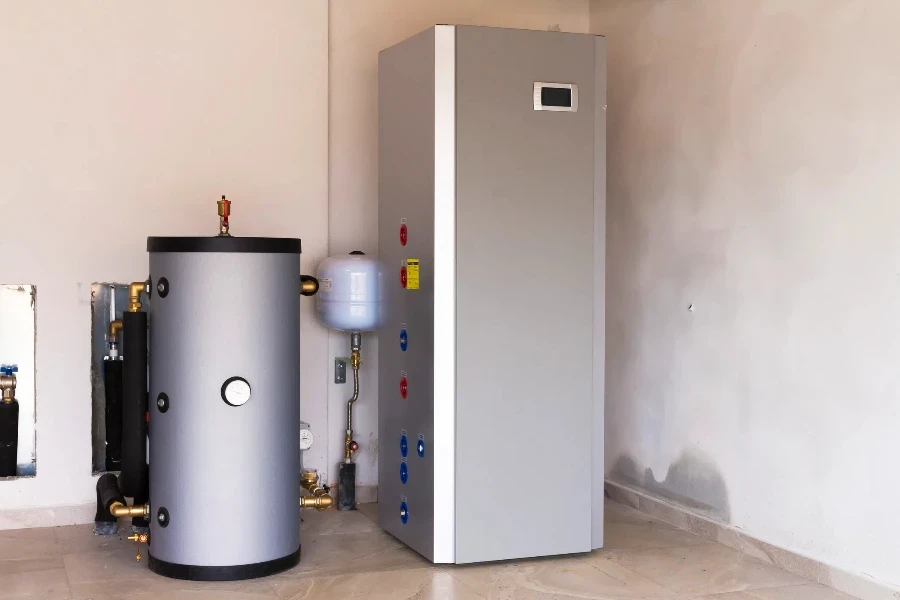

When investing in a heat pump water heater, it’s essential to evaluate not only the upfront cost but also the long-term savings and total cost of ownership. These systems tend to have higher initial costs compared to traditional electric or gas water heaters. However, the significant energy savings they offer can offset the initial investment over time.
Energy savings primarily result from the high efficiency of heat pump water heaters, which can reduce electricity consumption by up to 60% compared to conventional models. Additionally, many regions offer rebates and incentives for installing energy-efficient appliances, further lowering the overall cost.
Maintenance costs should also be considered. While heat pump water heaters generally require less frequent maintenance than traditional systems, periodic checks and servicing are necessary to ensure optimal performance. Over the unit’s lifespan, typically ranging from 10 to 15 years, these costs can add up but are often outweighed by energy savings.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
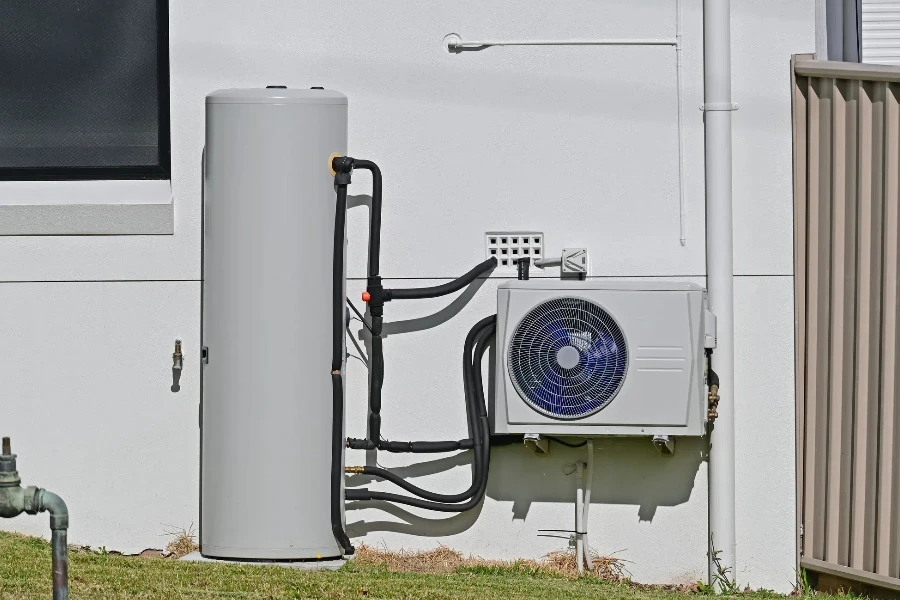

Compliance with industry standards and certifications is a critical consideration when selecting a heat pump water heater. These certifications ensure the product meets specific safety, performance, and energy efficiency criteria. Common certifications include ENERGY STAR, which signifies superior energy efficiency, and UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification, indicating compliance with safety standards.
Adherence to local building codes and regulations is essential for legal and safe installation. This may involve meeting specific requirements for electrical connections, ventilation, and water pressure. Ensuring the chosen model complies with these standards can prevent potential legal issues and safety hazards.
Compatibility with Existing Systems and Future Upgrades
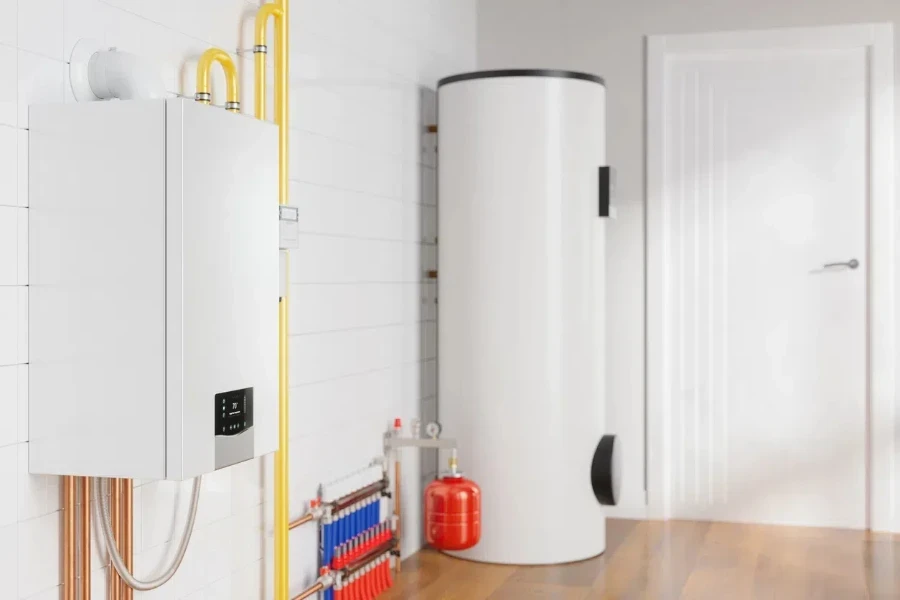

When integrating a heat pump water heater into an existing system, compatibility is a significant factor. It’s important to ensure the new unit can seamlessly connect with the current plumbing and electrical infrastructure. This may involve checking the voltage and amperage requirements, as well as the water inlet and outlet sizes.
Considering future upgrades is wise. Some heat pump water heaters are designed with modular components, allowing for easy upgrades and integration with renewable energy sources like solar panels. This future-proofing can enhance the system’s efficiency and sustainability, offering additional savings and environmental benefits.
Final Thoughts on Heat Pump Water Heaters
Selecting a heat pump water heater requires understanding various factors, from performance and efficiency to build quality and regulatory compliance. By carefully considering these aspects, you can make informed decisions that ensure optimal performance, long-term savings, and compliance with industry standards. The integration of advanced technological features and future-proofing options further enhances the value of these systems, making them a wise investment for both residential and commercial applications.




