Avanços recentes na impressão SLA revolucionaram as indústrias com soluções de impressão 3D de alta precisão. Este artigo se aprofunda nos fatores críticos a serem considerados ao selecionar uma impressora SLA, fornecendo aos compradores profissionais análises aprofundadas e insights valiosos para auxiliar na tomada de decisões informadas. Descubra como essas tecnologias podem elevar as capacidades de negócios e otimizar as operações.
Sumário:
– Visão geral do mercado de impressoras SLA
– Introdução e análise detalhada do mercado de impressoras SLA
– Fatores-chave ao selecionar uma impressora SLA
– Avanços na tecnologia de impressão SLA
– Aplicações práticas de impressoras SLA na indústria
– Tendências futuras na impressão SLA
– Encerrando
Visão geral do mercado de impressoras SLA
O mercado global de impressoras SLA (estereolitografia) tem visto um crescimento significativo nos últimos anos e espera-se que continue se expandindo. O valor de mercado era de aproximadamente US$ 1.8 bilhão em 2024 e está projetado para atingir US$ 3.5 bilhões até 2028, crescendo a uma taxa de crescimento anual composta (CAGR) de 11.5%. Esse crescimento é impulsionado pela crescente demanda por soluções de impressão 3D de alta precisão em vários setores, incluindo saúde, automotivo, aeroespacial e eletrônicos de consumo. A América do Norte detém a maior fatia de mercado, respondendo por aproximadamente 35% do mercado global, seguida pela Europa e pela região Ásia-Pacífico.
O setor de saúde é um grande impulsionador do mercado de impressoras SLA, com aplicações na fabricação de dispositivos médicos e odontológicos. As indústrias automotiva e aeroespacial também contribuem significativamente, alavancando a tecnologia SLA para prototipagem e produção de componentes leves e complexos. Além disso, a indústria de eletrônicos de consumo está adotando cada vez mais impressoras SLA para prototipagem rápida e produção em pequena escala. O mercado é altamente competitivo, com participantes importantes como 3D Systems, Formlabs e EnvisionTEC liderando a carga.
Iniciativas governamentais e investimentos em tecnologias avançadas de fabricação estão impulsionando ainda mais o mercado. Por exemplo, o programa Horizon 2020 da União Europeia alocou fundos substanciais para pesquisa e desenvolvimento em tecnologias de impressão 3D. Espera-se que a tendência crescente de digitalização e a integração da Indústria 4.0 criem novas oportunidades para o mercado de impressoras SLA nos próximos anos.
Introdução e análise detalhadas do mercado de impressoras SLA

As impressoras SLA são conhecidas por produzir peças complexas de alta resolução com excelentes acabamentos de superfície. Essas impressoras usam um laser para curar resina líquida em plástico sólido, camada por camada, permitindo a criação de geometrias complexas que são difíceis de serem alcançadas com métodos de fabricação tradicionais. Os principais benchmarks de desempenho para impressoras SLA incluem espessura de camada, velocidade de impressão, volume de construção e opções de material. As impressoras SLA de ponta podem atingir espessuras de camada tão finas quanto 25 mícrons, garantindo detalhes e precisão excepcionais.
Vários fatores influenciam a dinâmica do mercado, incluindo avanços em materiais de resina, melhorias na tecnologia laser e o desenvolvimento de software amigável. A mudança para práticas de fabricação sustentáveis também está impactando o mercado, com fabricantes focando em resinas ecológicas e impressoras com eficiência energética. O comportamento do consumidor está mudando para produtos personalizados, e as impressoras SLA são bem adequadas para atender a essa demanda devido à sua flexibilidade e precisão.
Os canais de distribuição para impressoras SLA incluem vendas diretas, plataformas on-line e distribuidores terceirizados. O aumento do comércio eletrônico tornou mais fácil para as empresas comprarem impressoras SLA e consumíveis relacionados, contribuindo para o crescimento do mercado. Inovações recentes no mercado incluem a introdução de impressoras SLA híbridas que combinam estereolitografia com outras tecnologias de impressão 3D, aumentando a versatilidade e o escopo de aplicação. O ciclo de vida do produto das impressoras SLA normalmente abrange vários anos, com atualizações regulares de software e avanços de material estendendo sua usabilidade.
Um dos principais desafios para os clientes é o alto custo inicial das impressoras SLA, que pode variar de US$ 3,000 a mais de US$ 100,000, dependendo das especificações. Além disso, o custo dos consumíveis, como resinas, pode aumentar ao longo do tempo. No entanto, os benefícios de longo prazo, incluindo tempo e custo de prototipagem reduzidos, geralmente superam esses investimentos iniciais. As estratégias de posicionamento da marca no mercado de impressoras SLA se concentram na confiabilidade, precisão e facilidade de uso. As estratégias de diferenciação incluem oferecer resinas especializadas para aplicações específicas, fornecer suporte abrangente ao cliente e desenvolver impressoras com volumes de construção maiores.
Os nichos de mercado para impressoras SLA incluem design de joias, onde a tecnologia é usada para criar moldes detalhados para fundição, e educação, onde as impressoras SLA são usadas para fins de ensino e pesquisa. A ênfase na digitalização e na fabricação inteligente está impulsionando a adoção de impressoras SLA nesses setores especializados.
Fatores-chave ao selecionar uma impressora SLA

Ao considerar a aquisição de uma impressora de estereolitografia (SLA), entender vários fatores é essencial para garantir que a impressora escolhida atenda às necessidades específicas do seu negócio. Esses fatores incluem os tipos de impressoras SLA disponíveis, especificações de desempenho, compatibilidade de materiais, qualidade de construção e considerações de custo. Cada elemento desempenha um papel crucial na determinação da eficácia geral e adequação da impressora para suas operações.
Tipos de impressoras SLA
As impressoras SLA vêm em várias configurações, cada uma projetada para diferentes aplicações e requisitos. As impressoras SLA de mesa são compactas e ideais para prototipagem em pequena escala e uso pessoal. Essas impressoras são normalmente mais acessíveis e fáceis de operar, tornando-as adequadas para pequenas empresas ou usuários individuais. As impressoras SLA industriais, por outro lado, são projetadas para fabricação em larga escala e produção de alto volume. Elas oferecem maiores volumes de construção, maior precisão e melhor durabilidade, atendendo a setores como automotivo, aeroespacial e saúde.
Outro tipo a ser considerado é a impressora SLA com tecnologia Digital Light Processing (DLP). As impressoras SLA baseadas em DLP usam uma tela de projetor para piscar uma camada inteira do objeto de uma vez, acelerando significativamente o processo de impressão. Isso as torna vantajosas para aplicações que exigem tempos de produção mais rápidos. Cada tipo de impressora SLA tem suas vantagens e limitações exclusivas, e selecionar a correta depende de suas necessidades específicas e metas de produção.
Especificações de performance
As especificações de desempenho são críticas para determinar a eficiência e a qualidade de saída de uma impressora SLA. As principais especificações incluem resolução de impressão, espessura da camada e volume de construção. A resolução de impressão, medida em mícrons, indica o nível de detalhes que a impressora pode atingir. Uma resolução mais alta se traduz em detalhes mais finos e superfícies mais suaves, cruciais para aplicações que exigem alta precisão, como modelos odontológicos ou designs de joias intrincados.
A espessura da camada, também medida em mícrons, afeta a suavidade do objeto impresso. Camadas mais finas resultam em superfícies mais lisas, mas aumentam o tempo de impressão. Equilibrar a espessura da camada com a velocidade de produção é essencial para otimizar a qualidade e a eficiência. O volume de construção determina o tamanho máximo do objeto que pode ser impresso. Garantir que a impressora tenha um volume de construção adequado para seus projetos é vital para evitar limitações nas capacidades de produção.
Compatibilidade de Material
As impressoras SLA usam resinas fotopolímero que endurecem após exposição à luz UV. A compatibilidade dessas resinas com a impressora é uma consideração importante. Diferentes resinas oferecem propriedades variadas, como flexibilidade, tenacidade e resistência ao calor. Por exemplo, resinas padrão são adequadas para prototipagem de uso geral, enquanto resinas de engenharia fornecem propriedades mecânicas aprimoradas para peças funcionais. Resinas odontológicas e biocompatíveis são formuladas especificamente para aplicações médicas, garantindo segurança e conformidade com os padrões da indústria.
Também vale a pena considerar a disponibilidade de resinas de terceiros. Algumas impressoras SLA são projetadas para trabalhar exclusivamente com resinas proprietárias, o que pode limitar as opções de materiais e aumentar os custos. Impressoras que suportam sistemas de materiais abertos oferecem maior flexibilidade e economia de custos ao permitir o uso de uma gama mais ampla de resinas de vários fornecedores.
Qualidade e durabilidade de construção
A qualidade de construção e a durabilidade de uma impressora SLA são fatores cruciais que impactam sua longevidade e confiabilidade. Impressoras de alta qualidade são construídas com materiais robustos e componentes projetados com precisão, garantindo desempenho consistente e tempo de inatividade reduzido. Recursos como estrutura rígida, óptica de alta qualidade e sistemas de movimento confiáveis contribuem para a durabilidade e precisão geral da impressora.
Além disso, a facilidade de manutenção e a disponibilidade de peças de reposição são considerações importantes. Impressoras com designs modulares e componentes substituíveis pelo usuário simplificam as tarefas de manutenção e minimizam as interrupções na produção. Avaliar a reputação do fabricante, o suporte ao cliente e a cobertura da garantia também pode fornecer insights sobre a confiabilidade de longo prazo da impressora.
Considerações sobre custos
O custo de uma impressora SLA abrange não apenas o preço de compra inicial, mas também as despesas operacionais contínuas. Os custos iniciais variam amplamente com base no tipo e nas capacidades da impressora. As impressoras SLA de mesa são geralmente mais acessíveis, com preços que variam de algumas centenas a vários milhares de dólares. As impressoras SLA industriais, com seus recursos avançados e maiores volumes de construção, podem custar dezenas de milhares de dólares.
Os custos operacionais incluem despesas com resinas, manutenção e consumíveis como peças de reposição e suprimentos de limpeza. Avaliar o custo por impressão e a eficiência da impressora pode ajudar a estimar o custo total de propriedade. Também é benéfico considerar o potencial retorno sobre o investimento (ROI) avaliando como a impressora pode aumentar a produtividade, reduzir os prazos de entrega e melhorar a qualidade do produto.
Avanços na tecnologia de impressão SLA
A tecnologia de impressão SLA tem visto avanços significativos nos últimos anos, aprimorando suas capacidades e expandindo suas aplicações. Um desenvolvimento notável é a melhoria na velocidade de impressão. As impressoras SLA tradicionais eram frequentemente criticadas por seus tempos de impressão lentos devido ao processo de cura camada por camada. No entanto, inovações recentes como a produção contínua de interface líquida (CLIP) reduziram drasticamente os tempos de impressão ao curar camadas continuamente, resultando em produção mais rápida sem comprometer a qualidade.
Outro avanço é o desenvolvimento de resinas mais sofisticadas com propriedades aprimoradas. Por exemplo, novas resinas de engenharia oferecem melhor resistência mecânica, resistência ao calor e flexibilidade, tornando-as adequadas para uma gama mais ampla de aplicações industriais. Além disso, os avanços em resinas biocompatíveis expandiram o uso da impressão SLA no campo médico, permitindo a produção de implantes personalizados, dispositivos odontológicos e guias cirúrgicos.
A automação e a integração com outros processos de fabricação também melhoraram. As impressoras SLA modernas são equipadas com recursos como dispensação automática de resina, monitoramento remoto e integração com software CAD, simplificando o fluxo de trabalho e reduzindo a intervenção manual. Esses avanços tornaram a impressão SLA mais eficiente, versátil e acessível a uma gama maior de indústrias.
Aplicações práticas de impressoras SLA na indústria

As impressoras SLA encontraram aplicações práticas em vários setores devido à sua capacidade de produzir peças altamente detalhadas e precisas. No setor de saúde, a impressão SLA é usada para criar alinhadores dentais personalizados, próteses e guias cirúrgicos. A alta resolução e a biocompatibilidade das peças impressas em SLA garantem que elas atendam aos rigorosos requisitos de aplicações médicas.
Nas indústrias automotiva e aeroespacial, as impressoras SLA são usadas para prototipagem rápida e produção de componentes complexos. A capacidade de produzir e iterar designs rapidamente permite que os engenheiros testem e refinem as peças antes de passar para a produção em massa. Isso acelera o processo de desenvolvimento e reduz os custos associados aos métodos tradicionais de fabricação.
A indústria de joias também se beneficia da precisão e do detalhe da impressão SLA. Os joalheiros podem criar designs e protótipos intrincados com alta precisão, permitindo a criação de peças personalizadas e reduzindo o tempo necessário para métodos tradicionais de artesanato. A impressão SLA também permite a produção de padrões mestres para fundição de investimento, simplificando ainda mais o processo de fabricação.
Tendências futuras em impressão SLA
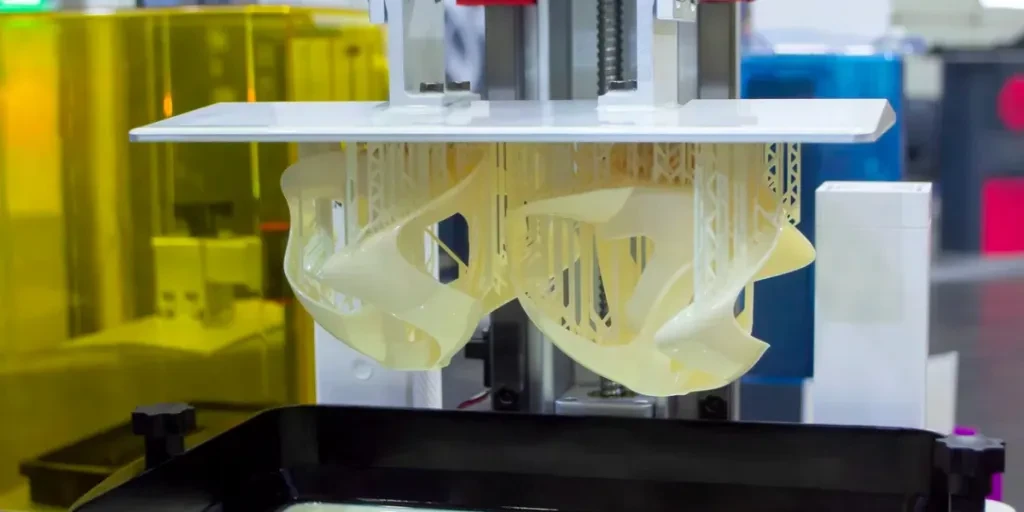

O futuro da impressão SLA parece promissor, com várias tendências prontas para moldar sua evolução. Uma tendência-chave é o desenvolvimento de capacidades de impressão multimaterial. Pesquisadores estão trabalhando em impressoras SLA que podem imprimir simultaneamente com múltiplas resinas, permitindo a criação de peças complexas com propriedades variadas. Esse avanço abrirá novas possibilidades para designs inovadores e protótipos funcionais.
Outra tendência é a integração de inteligência artificial (IA) e aprendizado de máquina na impressão SLA. Algoritmos de IA podem otimizar as configurações de impressão, prever problemas potenciais e melhorar a qualidade da impressão, reduzindo a necessidade de ajustes manuais e aumentando a eficiência geral. O aprendizado de máquina também pode permitir manutenção preditiva, minimizando o tempo de inatividade e estendendo a vida útil da impressora.
A sustentabilidade também está se tornando um foco significativo na indústria de impressão SLA. Esforços estão sendo feitos para desenvolver resinas ecologicamente corretas e reduzir o desperdício por meio da melhoria dos processos de reciclagem. A adoção de práticas sustentáveis não só beneficiará o meio ambiente, mas também se alinhará à crescente demanda por soluções de fabricação ambientalmente responsáveis.
Resumindo
Em resumo, selecionar a impressora SLA certa requer consideração cuidadosa de vários fatores, incluindo o tipo de impressora, especificações de desempenho, compatibilidade de material, qualidade de construção e custo. Entender esses elementos garante que a impressora escolhida atenda às suas necessidades específicas e forneça os resultados desejados. Os avanços na tecnologia de impressão SLA continuam a aprimorar suas capacidades e expandir suas aplicações, tornando-a uma ferramenta valiosa em vários setores. À medida que a tecnologia evolui, tendências futuras como impressão multimaterial, integração de IA e sustentabilidade moldarão ainda mais o cenário da impressão SLA, oferecendo novas oportunidades de inovação e eficiência.





 Afrikaans
Afrikaans አማርኛ
አማርኛ العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Kiswahili
Kiswahili ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt isiXhosa
isiXhosa Zulu
Zulu