Hydraulic presses, the backbone of the manufacturing industry, have revolutionized how materials are shaped, formed, and pressed. These machines apply a significant amount of pressure to mold materials into specific shapes, making them indispensable in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and metalworking. This article aims to demystify hydraulic presses, breaking down their complexities into understandable segments, addressing common questions, and providing insights into their operation, types, benefits, maintenance, and safety considerations.
Table of Contents:
– What are hydraulic presses and how do they work?
– Types of hydraulic presses and their applications
– Key benefits of using hydraulic presses in manufacturing
– Maintenance tips for hydraulic presses
– Safety considerations for operating hydraulic presses
What are hydraulic presses and how do they work?
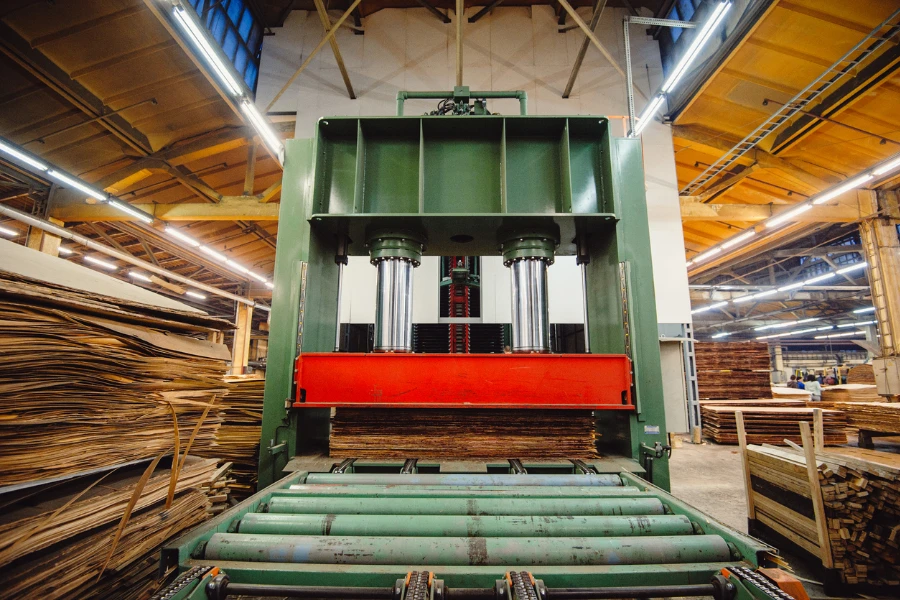

Hydraulic presses function on the principle of Pascal’s law; that is, when pressure is applied to a fluid in a closed system, the pressure is distributed equally in all directions. This principle allows a hydraulic press to generate a large force with a relatively small input force. At its core, a hydraulic press consists of two cylinders: a larger master cylinder and a smaller slave cylinder. Hydraulic fluid, usually oil, is compressed in the master cylinder, which in turn exerts pressure on the slave cylinder. The force generated can be immense, making hydraulic presses suitable for tasks requiring high pressure, such as metal forming.
Understanding the mechanics of hydraulic presses involves recognizing the role of components like pumps, valves, and pistons. These components work together seamlessly to control the movement of the hydraulic fluid, thereby controlling the pressure applied. The versatility of hydraulic presses comes from the ability to adjust the pressure and speed, making them adaptable to various materials and applications.
The evolution of hydraulic presses has led to increased efficiency and precision. Modern hydraulic presses are equipped with sophisticated controls and sensors that ensure consistent quality and safety. This evolution reflects the ongoing innovation in hydraulic technology, aiming to meet the ever-growing demands of the manufacturing industry.
Types of hydraulic presses and their applications
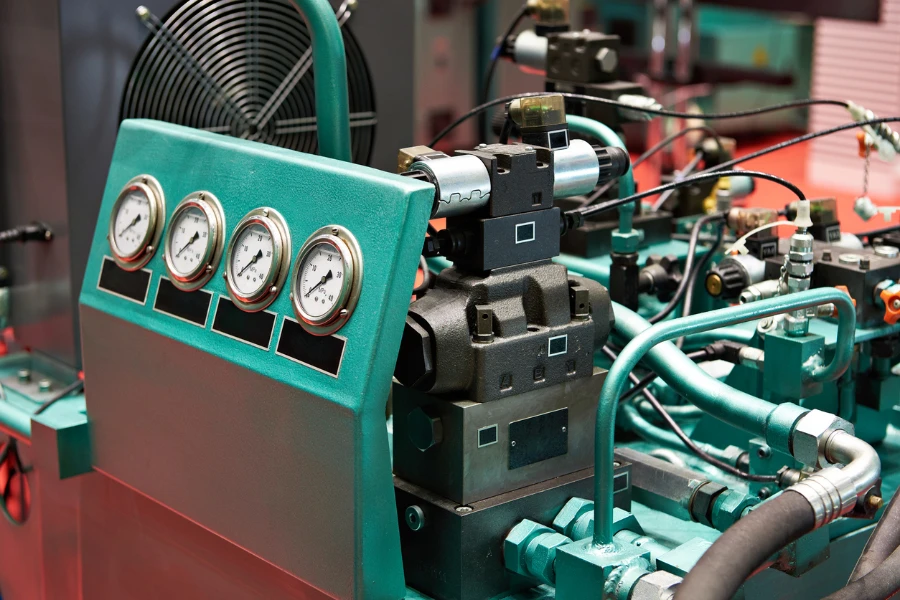
Hydraulic presses come in various designs, each tailored to specific tasks. The most common types include the C-frame press, H-frame press, and the four-column press. C-frame presses, known for their open C-shaped frame, offer excellent accessibility and are commonly used for assembly, straightening, and drawing operations. H-frame presses, or floor presses, are characterized by their robust construction and are suited for heavy-duty pressing operations.
Four-column presses, with their four-post construction, provide uniform pressure distribution and are widely used for applications requiring precision, such as molding and deep drawing. Each type of hydraulic press has its unique advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the task at hand.
The applications of hydraulic presses are vast and varied. In the automotive industry, they are used for stamping car body parts, while in the aerospace sector, they play a crucial role in forming aircraft components. In the metalworking industry, hydraulic presses are indispensable for tasks such as forging, clinching, and blanking. The versatility and adaptability of hydraulic presses make them a valuable asset in any manufacturing process.
Key benefits of using hydraulic presses in manufacturing
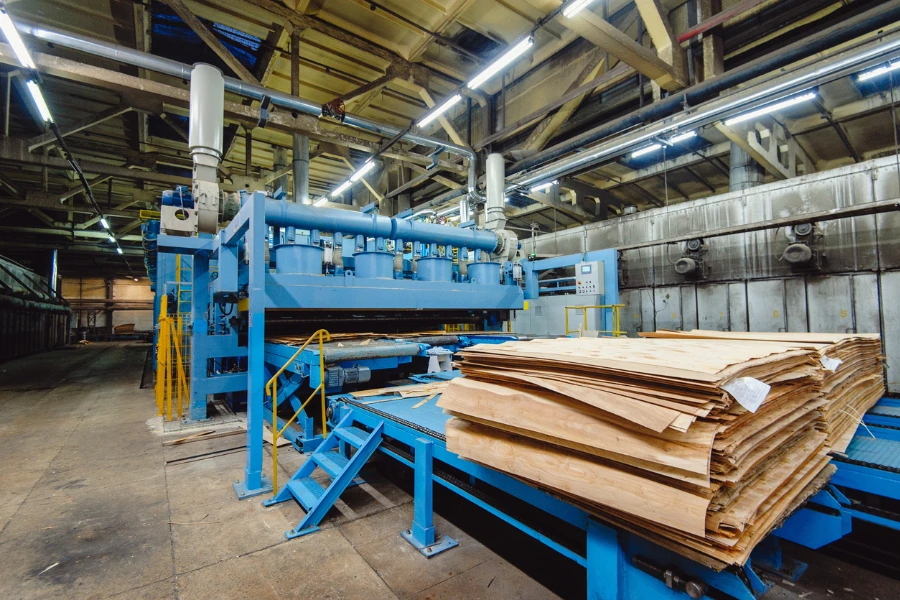

Hydraulic presses offer several advantages over mechanical presses, including higher pressure capacity, greater versatility, and more precise control. One of the key benefits is the ability to achieve uniform pressure application, essential for ensuring consistent product quality. Additionally, the flexibility to adjust pressure and speed allows for a wide range of materials to be processed, from metals to plastics.
Another significant advantage is energy efficiency. Hydraulic presses consume power only during the pressing cycle, unlike mechanical presses that run continuously. This on-demand operation leads to significant energy savings, reducing operational costs. Furthermore, the simplicity of hydraulic systems results in lower maintenance requirements, enhancing the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Maintenance tips for hydraulic presses
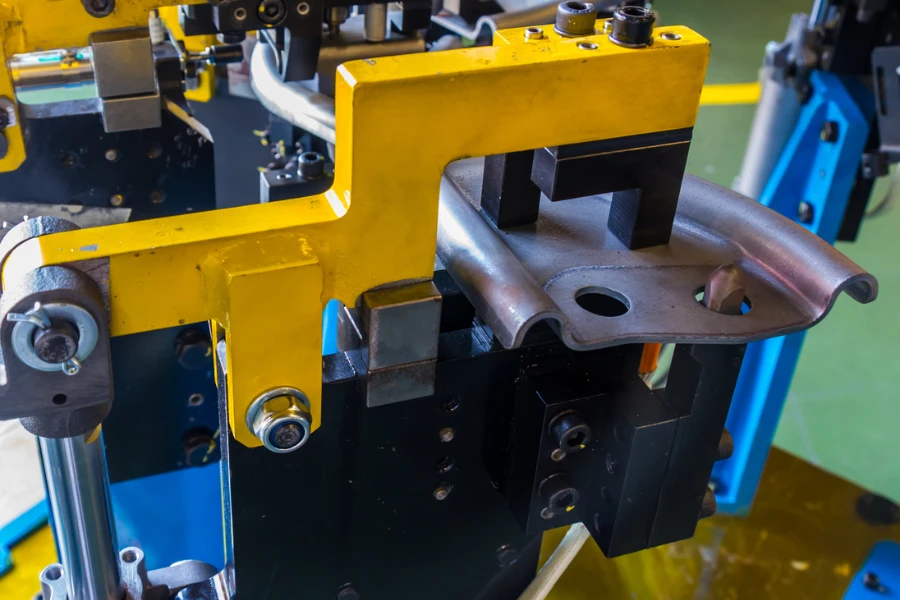
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of hydraulic presses. Regularly checking and replacing hydraulic fluid can prevent contamination that could lead to system failures. Monitoring system pressure and inspecting hoses and seals for leaks are also essential practices. These steps help in maintaining the optimal performance of the press and preventing unscheduled downtime.
Lubrication of moving parts is another critical aspect of maintenance. Adequate lubrication reduces friction, preventing wear and extending the life of the components. Additionally, keeping the hydraulic press clean from debris and dust can prevent potential operational issues. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule is the best way to ensure the press remains in good working condition, contributing to smoother and more efficient operations.
Safety considerations for operating hydraulic presses

Safety is paramount when operating hydraulic presses. Proper training for operators is essential to ensure they understand the operation and potential hazards of the machine. Utilizing safety guards and barriers can prevent accidental contact with moving parts. Additionally, implementing safety protocols, such as lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance, can protect against unexpected activations.
Emergency stop buttons should be easily accessible to allow for immediate shutdowns in case of an emergency. Regular safety inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can further enhance the safe operation of hydraulic presses. By prioritizing safety, manufacturers can protect their employees and equipment, promoting a productive and accident-free work environment.
Conclusion
Hydraulic presses play a pivotal role in the manufacturing industry, offering versatility, efficiency, and precision. Understanding their operation, types, and maintenance can help manufacturers leverage these machines to their full potential. By adhering to safety practices, businesses can ensure a safe and productive environment. As technology advances, hydraulic presses will continue to evolve, further enhancing their capabilities and applications in the industry.




