Polyethylene (PE for short) is a thermoplastic resin made by polymerizing ethylene. It also includes copolymers of ethylene with a small amount of α-olefin. Polyethylene has many advantages, such as an odorless, non-toxic, wax-like feel, good low-temperature resistance, good chemical stability, and the ability to withstand the erosion of most acids and alkalis. At room temperature, it is insoluble in general solvents, has less water absorption, and has good electrical insulation properties.

Polyethylene is a semi-crystalline polymer compound that can be polymerized with ethylene monomer by high-pressure, medium-pressure and low-pressure methods. In addition, fluidized bed vapor phase, slurry and solution methods are available to produce linear low density polyethylene.
Depending on the density, polyethylene can be classified into types such as ultra-low density polyethylene (ULDPE), low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), medium density polyethylene (MDPE) and high density polyethylene (HDPE).
Depending on the method of polymer synthesis, polyethylene can be classified into high-pressure polyethylene (polyethylene made at 101.3354.6 MPa), medium-pressure polyethylene (2.17.1 MPa) and low-pressure polyethylene (0.1 to 2.1 MPa).
Depending on the relative molecular mass, polyethylene can be divided into medium relative molecular mass (5.25 million, common in the industry and used for general purpose products), high relative molecular mass (about 500,000), ultra-high relative molecular mass (1,001,500,000), and ultra-low relative molecular mass (about 10,000, mainly used as lubricants and dispersing agents for plastics molding).
Depending on the structure of the polymer molecular chain, polyethylene can be classified into linear polyethylene (e.g. HDPE, MDPE, LLDPE, VLLDPE, ULLDPE, MLLDPE, EPPE, UHMWPE) and branched polyethylene (LDPE).
1. Ultra-low density polyethylene (ULDPE)
Ultra-low density polyethylene (ULDPE), or ULDPE for short, is a polymer whose polymerization mechanism is similar to that of LLDPE in that it has a linear structure with no long chain branches. For this reason, ULDPE is also known as the second generation of LLDPE. Compared to LLDPE, ULDPE has more short branched chains, and the branched chains are shorter and more regular than those of LDPE, and do not contain long chain branches. It has a narrower molecular weight distribution and a different crystal phase structure and degree of entanglement than LDPE. The presence of a large number of short chain branches in ULDPE films weakens the formation of crystalline zones in the polymer main chain. When crystalline regions are formed, the crystalline regions are deformed, resulting in defects. Under the same crystallization conditions, the crystalline structure of ULDPE is significantly different, resulting in products with very different physical and mechanical properties from other polyethylenes.
ULDPE is characterized by:
- Excellent tensile strength, impact strength, tear strength, and puncture resistance.
- Thermal properties: Due to VLPDE and ULDPE being short-chain linear crystalline, compared to the long-chain branched LDPE, their crystal structure defects are less pronounced, hence a higher melting point, about 20°C higher than EVA copolymers, resulting in a higher service temperature for their products.
- Modulus: U/VLDPE has a lower modulus compared to LDPE, LLDPE, and HDPE, making its films tough, flexible, and soft to the touch.
- Compatibility: U/VLDPE blends well with other polyolefins, showing good compatibility.
- Other properties: U/VLDPE exhibits excellent down-gauging capability (reaching 10-12.7um), good insulation, optical properties, chemical resistance, oil resistance, and sealability.
In terms of applications:
In terms of defense munitions equipment, because ULDPE has good impact resistance and large specific energy absorption capacity, can be used for the manufacture of protective clothing, helmets, ballistic materials, such as helicopters, tanks and ships, armor protection plates, radar protection shell cover, missile cover, bulletproof vests, anti-stabbing vests, shields, parachutes and so on.
In aerospace engineering, ULDPE is suitable for wingtip structures of various aircraft, airship structures and buoy aircraft due to its light weight, high strength and good impact resistance.
In the civil sector, ULDPE can be made into ropes, cables, sails and fishing gear for marine engineering. Under dead weight, the breaking length of ULDPE ropes is 8 times longer than steel ropes and 2 times longer than aramid. The ropes can be used as fixed anchor ropes for supertankers, offshore operating platforms, lighthouses and so on.
In industrial applications, ULDPE can be used as pressure-resistant containers, conveyor belts, filtration materials, automotive cushioning boards, etc.; in the construction field, it can be used for walls, partition structures, etc. In the machinery manufacturing industry, ULDPE is widely used to make all kinds of gears, cams, impellers, rollers, pulleys, bearings, axle tiles, bushings, clipped shafts, gaskets, sealing gaskets, elastic couplings, screws and other mechanical parts.
In sporting goods, ULDPE has been made into helmets, skis, windsurfing boards, fishing rods, racquets, as well as bicycles, gliding boards, and ultra-lightweight aircraft parts.
In the medical field, ULDPE is used in dental tray materials, medical implants and orthopedic sutures. It has good biocompatibility and durability with high stability and does not cause allergic reactions. Therefore, ULDPE has been widely used in clinical applications. In addition, it is used in the manufacture of medical gloves and other medical measures, among others.

2. Low density polyethylene (LDPE)
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic produced by free radical polymerization of ethylene under high pressure. This material is in the form of milky-white round bead-shaped particles, non-toxic, tasteless, odorless and with a non-glossy surface. Its density ranges from 0.916 to 0.930 g/cm³.LDPE has softer properties, as well as good ductility, electrical insulation, chemical stability, processability, and low-temperature resistance (up to -70°C). However, its mechanical strength, moisture barrier, air barrier and solvent resistance are poor. Its molecular structure is not regular enough, its crystallinity is low (55%~65%), and its crystalline melting point is low (108~126℃).
LDPE combines some excellent characteristics, such as high transparency, chemical inertness, good closure, and easy molding and processing. Therefore, it is widely used in the polymer industry.
LDPE is suitable for various thermoplastic molding processes, such as injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, rotational molding, coating, foaming, thermoforming, hot air welding, heat welding and so on.
LDPE is mainly used to make film products such as agricultural films, ground cover films, agricultural films, and vegetable greenhouse films. It is also used in packaging films for confectionery, vegetables, frozen foods and more. In addition, LDPE can be used in blow molded films for liquid packaging (e.g. milk, soy sauce, fruit juice, tofu and soya milk); heavy-duty bags, shrink wrap films, elastic films and liner films; films for construction, general industrial packaging films and food bags etc. LDPE can also be used in injection molded products such as small containers, lids, daily necessities, plastic flowers, and injection stretch blow molded containers. It can also be used in medical devices, pharmaceutical and food packaging materials, extruded pipes, plates, wire and cable wrapping, profiles, thermoformed products, etc. Blow molded hollow molded products can also be made of LDPE, such as dairy and jam containers, medicines, cosmetics, chemical product containers, tanks and so on.

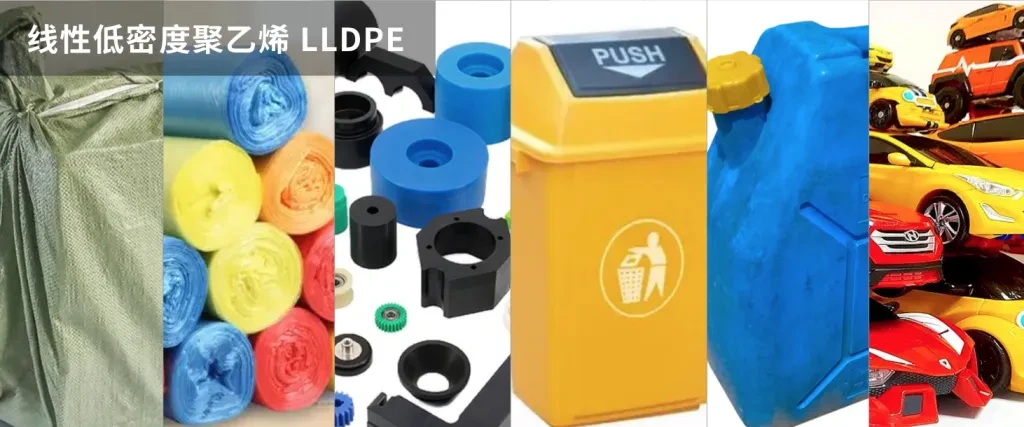
3. Linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE)
Linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) is a plastic produced by the co-polymerisation of ethylene and higher alpha olefins such as butene, hexene or octene at much lower temperatures and pressures. LLDPE has a narrow molecular weight distribution and linear structure that gives it different rheological properties compared to typical low density polyethylene (LDPE).
LLDPE is milky white granule, non-toxic, tasteless and odorless. Its density is 0.918~0.935g/cm³. Compared with LDPE, LLDPE has higher softening and melting temperatures, better strength, toughness, rigidity, heat and cold resistance, and good resistance to environmental stress cracking, impact strength and tear strength. In addition, LLDPE is also resistant to acids, alkalis and organic solvents, and is widely used in industry, agriculture, medicine, health and daily necessities.
In terms of applications, LLDPE is used in a wide range of film markets, such as the production of bags, rubbish bags, elastic wrappers, industrial liners, towel liners and shopping bags. These applications take advantage of the improved strength and toughness of LLDPE resin. Injection molding and rotational molding are the most common molding applications for LLDPE, and its superior toughness and low-temperature impact strength make it theoretically suitable for products such as waste bins, toys and refrigerated appliances.

4. Medium density polyethylene (MDPE)
Medium density polyethylene (MDPE) is a plastic between high density polyethylene (HDPE) and low density polyethylene (LDPE), which has both the rigidity of HDPE and the flexibility and creep resistance of LDPE, combining the advantages of both. MDPE is a resin made from the co-polymerization of ethylene and octene, with a special linear ethylene backbone and octene branched chains, which provides excellent toughness and long-term water pressure resistance.
The synthetic process for the production of MDPE adopts the method of LLDPE. Commonly used alpha olefins include propylene, 1-butene, 1-hexene and 1-octene, etc. The amount of olefin used affects the size of the density, and the amount of olefin is generally about 5% (mass fraction). MDPE can be produced by extrusion, injection, blow-molding, rotational, rotational and powder molding, etc., and the parameters of its production process are similar to those of HDPE and LDPE.
MDPE introduces an average of 20 methyl or 13 ethyl chains per 1000 carbon atoms in the main chain of the molecule, with different numbers and lengths of branches affecting the change in properties. Copolymerization increases the number of chains connecting the small pieces of crystal.
MDPE has resistance to environmental stress cracking and long-term retention of strength. Its relative density is 0.926-0.953g/cm³, crystallinity is 70%-80%, average molecular weight is 200,000, tensile strength is 8-24 MPa, elongation at break is 50%-60%, melt temperature is 126-135°C, melt flow rate is 0.1-35 g/10 min, and heat distortion temperature (0.46 MPa) is 49-74°C.
MDPE can be used in the fields of pipes, films, hollow containers and so on. The products can be used for high-speed molding of various bottles, high-speed automatic packaging films, various injection molding products, rotational molding products, wire and cable coverings, waterproof materials, water pipes, gas pipes and so on.

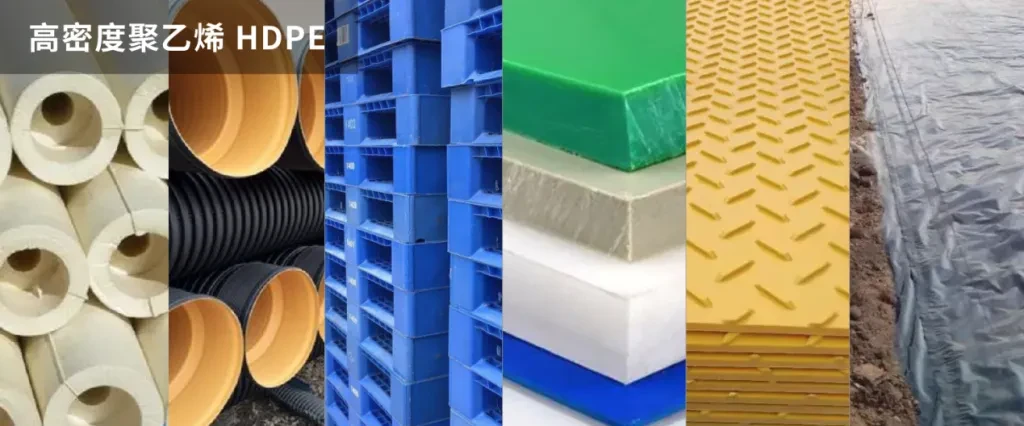
5. High density polyethylene (HDPE)
High density polyethylene (HDPE) is a non-toxic, non-smelly, odorless white particles, with a melting point of about 130°C and a relative density of 0.941-0.960g/cm 3. It has good heat resistance and cold resistance, chemical stability, as well as high rigidity and toughness, good mechanical strength, dielectric properties, and resistance to environmental stress cracking. The melting temperature is 120-160°C. For materials with larger molecules, the recommended melting temperature range is between 200-250°C.
HDPE is produced through a polymerization process with an ionic reaction mechanism. Depending on the initiator used and the reaction pressure, it is divided into low-pressure and medium-pressure methods, resulting in products with high molecular weight, short and few branches, hence high crystallinity and density. The polymerization conditions for the low-pressure method are: pressure 0.1-1.5 MPa, temperature within 65-100°C, using a Ziegler-Natta type initiator: Al(C2H5)3-TiCl4. The polymerization reaction mechanism is of a coordinative anionic nature. HDPE is suitable for various thermoplastic molding processes due to its good moldability, such as injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, rotational molding, coating, foaming processes, thermoforming, heat seal welding, thermal welding, etc.
Its main advantages include acid and alkali resistance, organic solvent resistance, excellent electrical insulation, and maintaining a certain level of toughness at low temperatures. Its surface hardness, tensile strength, rigidity, and other mechanical strengths are higher than LDPE, close to PP, more tough than PP, but with a lower surface glossiness than PP. The main disadvantages are poor mechanical performance, poor breathability, prone to deformation, aging, brittleness, lower brittleness than PP, prone to stress cracking, low surface hardness, prone to scratches. It is difficult to print on, requiring surface corona treatment for printing, cannot be electroplated, and has a matte surface.
Applications of high-density polyethylene HDPE:
- Injection molded products: turnover boxes, bottle caps, barrels, caps, food containers, trays, trash cans, boxes, and plastic flowers.
- Blow molded products: hollow molded products such as various series of blow molding barrels, containers, bottles, containing cleaners, chemicals, cosmetics, gasoline tanks, daily necessities, etc. Also includes film products like food packaging bags, sundry shopping bags, fertilizer lining films, etc.
- Extruded products: pipes and fittings mainly used in gas transmission, public water and chemical transportation, such as building material drainage pipes, gas pipes, hot water pipes, etc.; sheet materials mainly used for seats, suitcases, handling containers, etc.
- Rotational molding: injection-molded products such as large containers, storage tanks, barrels, boxes, etc.
- It can be processed into films, wire and cable sheaths, pipes, various hollow products, injection molded products, fibers, etc. Widely used in agriculture, packaging, electronics, machinery, automobiles, daily necessities, and other areas.

Disclaimer: The information set forth above is provided by Shanghai Qishen Plastic Industry independently of Chovm.com. Chovm.com makes no representation and warranties as to the quality and reliability of the seller and products.




 বাংলা
বাংলা Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu മലയാളം
മലയാളം پښتو
پښتو فارسی
فارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Kiswahili
Kiswahili ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt isiXhosa
isiXhosa Zulu
Zulu